The RNA-binding protein fragile X-related 1 regulates somite formation in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 16000371
- PMCID: PMC1196343
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0304
The RNA-binding protein fragile X-related 1 regulates somite formation in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
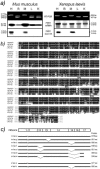
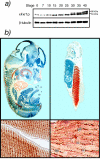
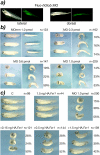
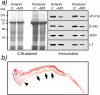
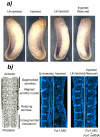
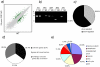
Fragile X-related 1 protein (FXR1P) is a member of a small family of RNA-binding proteins that includes the Fragile X mental retardation 1 protein (FMR1P) and the Fragile X-related 2 protein (FXR2P). These proteins are thought to transport mRNA and to control their translation. While FMR1P is highly expressed in neurons, substantial levels of FXR1P are found in striated muscles and heart, which are devoid of FMRP and FXR2P. However, little is known about the functions of FXR1P. We have isolated cDNAs for Xenopus Fxr1 and found that two specific splice variants are conserved in evolution. Knockdown of xFxr1p in Xenopus had highly muscle-specific effects, normal MyoD expression being disrupted, somitic myotomal cell rotation and segmentation being inhibited, and dermatome formation being abnormal. Consistent with the absence of the long muscle-specific xFxr1p isoform during early somite formation, these effects could be rescued by both the long and short mRNA variants. Microarray analyses showed that xFxr1p depletion affected the expression of 129 known genes of which 50% were implicated in muscle and nervous system formation. These studies shed significant new light on Fxr1p function(s).
Figures



References
-
- Bakker, C. E., and The Dutch-Belgian Fragile X Consortium. (1994). Fmr1 knockout mice: a model to study fragile X mental retardation. Cell 78, 23-33. - PubMed
-
- Bakker, C. E., De Diego Otero, Y., Bontekoe, C., Raghoe, P., Luteijn, T., Hoogeveen, A. T., Oostra, B. A., and Willemsen, R. (2000). Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization of FMRP, FXR1P, and FXR2P in the mouse. Exp. Cell Res. 258, 162-170. - PubMed
-
- Bardoni, B., and Mandel, J.-L. (2002). Advances in understanding of fragile X pathogenesis and FMRP function, and in identification of X linked mental retardation genes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12, 284-293. - PubMed
-
- Bisson, N., Islam, N., Poitras, L., Jean, S., Bresnick, A., and Moss, T. (2003). The catalytic domain of xPAK1 is sufficient to induce myosin II dependent in vivo cell fragmentation independently of other apoptotic events. Dev. Biol., 263, 264-281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

