Differential distribution and expression of Panton-Valentine leucocidin among community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
- PMID: 16000462
- PMCID: PMC1169154
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.7.3373-3379.2005
Differential distribution and expression of Panton-Valentine leucocidin among community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
Abstract
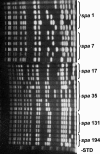
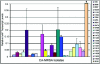
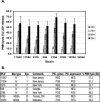
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) is an emerging threat worldwide. CA-MRSA strains differ from hospital-acquired MRSA strains in their antibiotic susceptibilities and genetic backgrounds. Using several genotyping methods, we clearly define CA-MRSA at the genetic level and demonstrate that the prototypic CA-MRSA strain, MW2, has spread as a homogeneous clonal strain family that is distinct from other CA-MRSA strains. The Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL)-encoding genes, lukF and lukS, are prevalent among CA-MRSA strains and have previously been associated with CA-MRSA infections. To better elucidate the role of PVL in the pathogenesis of CA-MRSA, we first analyzed the distribution and expression of PVL among different CA-MRSA strains. Our data demonstrate that PVL genes are differentially distributed among CA-MRSA strains and, when they are present, are always transcribed, albeit with strain-to-strain variability of transcript levels. To directly test whether PVL is critical for the pathogenesis of CA-MRSA, we evaluated the lysis of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) during phagocytic interaction with PVL-positive and PVL-negative CA-MRSA strains. Unexpectedly, there was no correlation between PVL expression and PMN lysis, suggesting that additional virulence factors underlie leukotoxicity and, thus, the pathogenesis of CA-MRSA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coexistence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive and -negative community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA400 sibling strains in a large Canadian health-care region.J Infect Dis. 2008 Jan 15;197(2):195-204. doi: 10.1086/523763. J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18173361
-
The emergence and importation of diverse genotypes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) harboring the Panton-Valentine leukocidin gene (pvl) reveal that pvl is a poor marker for community-acquired MRSA strains in Ireland.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Aug;45(8):2554-63. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00245-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17581935 Free PMC article.
-
Polyclonal emergence and importation of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains harbouring Panton-Valentine leucocidin genes in Belgium.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Dec;56(6):1103-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki379. Epub 2005 Oct 13. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16223937
-
Virulence determinants in community and hospital meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Hosp Infect. 2007 Jun;65 Suppl 2:105-9. doi: 10.1016/S0195-6701(07)60025-5. J Hosp Infect. 2007. PMID: 17540252 Review.
-
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: the role of Panton-Valentine leukocidin.Lab Invest. 2007 Jan;87(1):3-9. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700501. Epub 2006 Dec 4. Lab Invest. 2007. PMID: 17146447 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of ribotyping to retrospectively identify methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from phase 3 clinical trials for tigecycline that are genotypically related to community-associated isolates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Nov;49(11):4521-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.11.4521-4529.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16251291 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative genomics of Canadian epidemic lineages of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Jun;45(6):1904-11. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02500-06. Epub 2007 Apr 11. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17428941 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of kinase modulators as host-directed therapeutics against intracellular methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 25;14:1367938. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1367938. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38590439 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent nasal carriage with Staphylococcus aureus within a menstrual cycle: Results from a prospective cohort of healthy carriers.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(26):e4040. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004040. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27368032 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of the global regulators Agr and SaeRS in the pathogenesis of CA-MRSA USA300 infection.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 2;5(12):e15177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015177. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21151999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Boyum, A. 1968. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 97:77-89. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1999. Four pediatric deaths from community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Minnesota and North Dakota, 1997-1999. JAMA 282:1123-1125. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1999. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) System report, data summary from January 1990-May 1999, issued June 1999. Am. J. Infect. Control 27:520-532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

