Progressive degeneration of human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells triggered by dopamine-dependent oxidative stress is dependent on the mixed-lineage kinase pathway
- PMID: 16000623
- PMCID: PMC6725277
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1746-05.2005
Progressive degeneration of human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells triggered by dopamine-dependent oxidative stress is dependent on the mixed-lineage kinase pathway
Abstract
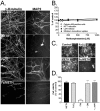
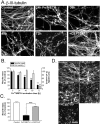
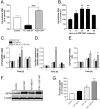
Models of Parkinson's disease (PD) based on selective neuronal death have been used to study pathogenic mechanisms underlying nigral cell death and in some instances to develop symptomatic therapies. For validation of putative neuroprotectants, a model is desirable in which the events leading to neurodegeneration replicate those occurring in the disease. We developed a human in vitro model of PD based on the assumption that dysregulated cytoplasmic dopamine levels trigger cell loss in this disorder. Differentiated human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells were exposed to methamphetamine (METH) to promote cytoplasmic dopamine accumulation. In the presence of elevated iron concentrations, as observed in PD, increased cytosolic dopamine led to oxidative stress, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway activation, neurite degeneration, and eventually apoptosis. We examined the role of the mixed-lineage kinases (MLKs) in this complex degenerative cascade by using the potent inhibitor 3,9-bis[(ethylthio)methyl]-K-252a (CEP1347). Inhibition of MLKs not only prevented FeCl2+/METH-induced JNK activation and apoptosis but also early events such as neurite degeneration and oxidative stress. This broad neuroprotective action of CEP1347 was associated with increased expression of an oxidative stress-response modulator, activating transcription factor 4. As a functional consequence, transcription of the cystine/glutamate and glycine transporters, cellular cystine uptake and intracellular levels of the redox buffer glutathione were augmented. In conclusion, this new human model of parkinsonian neurodegeneration has the potential to yield new insights into neurorestorative therapeutics and suggests that enhancement of cytoprotective mechanisms, in addition to blockade of apoptosis, may be essential for disease modulation.
Figures




References
-
- Acikgoz O, Gonenc S, Gezer S, Kayatekin BM, Uysal N, Semin I, Gure A (2001) Methamphetamine causes depletion of glutathione and an increase in oxidized glutathione in the rat striatum and prefrontal cortex. Neurotox Res 3: 277-280. - PubMed
-
- Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N, Nissou M, Benabid AL, Sadoul R, Verna JM (2001) Molecular pathways involved in the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol 65: 135-172. - PubMed
-
- Boll JB, Geist MA, Kaminski Schierle GS, Petersen K, Leist M, Vaudano E (2004) Improvement of embryonic dopaminergic neurone survival in culture and after grafting into the striatum of hemiparkinsonian rats by CEP-1347. J Neurochem 88: 698-707. - PubMed
-
- Borasio GD, Horstman S, Anneser JM, Neff NT, Glicksman MA (1990) CEP-1347/KT7515, a JNK pathway inhibitor, supports the in vitro survival of chick embryonic neurons. NeuroReport 9: 1435-1439. - PubMed
-
- Bozyczko-Coyne D, O'Kane TM, Wu ZL, Dobrzanski P, Murthy S, Vaught JL, Scott RW (2001) CEP-1347/KT-7515, an inhibitor of SAPK/JNK pathway activation, promotes survival and blocks multiple events associated with Abeta-induced cortical neuron apoptosis. J Neurochem 77: 849-863. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
