A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 16000631
- PMCID: PMC6725288
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1563-05.2005
A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2005 Nov 9;25(45):10576
Abstract
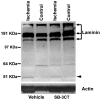
Neuronal cell death occurs during many neurodegenerative disorders and stroke. The aberrant, excessive activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), especially MMP-9, contributes directly to neuron apoptosis and brain damage (Rosenberg et al., 1996; Asahi et al., 2001; Gu et al., 2002; Horstmann et al., 2003). We determined that MMP-9 degrades the extracellular matrix protein laminin and that this degradation induces neuronal apoptosis in a transient focal cerebral ischemia model in mice. We also determined that the highly specific thiirane gelatinase inhibitor SB-3CT blocks MMP-9 activity, including MMP-9-mediated laminin cleavage, thus rescuing neurons from apoptosis. We conclude that MMP-9 is a highly promising drug target and that SB-3CT derivatives have significant therapeutic potential in stroke patients.
Figures
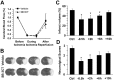
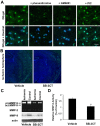
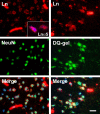

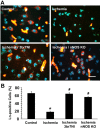


References
-
- Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ, Fini ME, Lo EH (2000) Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20: 1681-1689. - PubMed
-
- Brown S, Bernardo MM, Li ZH, Kotra LP, Tanaka Y, Fridman R, Mobashery S (2000) Potent and selective mechanism-based inhibition of gelatinases. J Am Chem Soc 122: 6799-6800.
-
- Castellanos M, Leira R, Serena J, Pumar JM, Lizasoain I, Castillo J, Davalos A (2003) Plasma metalloproteinase-9 concentration predicts hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34: 40-46. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZL, Strickland S (1997) Neuronal death in the hippocampus is promoted by plasmin-catalyzed degradation of laminin. Cell 91: 917-925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
