A phase 1/2 trial of high-dose yttrium-90-ibritumomab tiuxetan in combination with high-dose etoposide and cyclophosphamide followed by autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with poor-risk or relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 16002426
- PMCID: PMC1895300
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1310
A phase 1/2 trial of high-dose yttrium-90-ibritumomab tiuxetan in combination with high-dose etoposide and cyclophosphamide followed by autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with poor-risk or relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
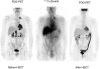
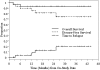
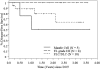
We conducted a phase 1/2 trial of high-dose 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan in combination with high-dose etoposide (VP-16) 40 to 60 mg/kg (day -4) and cyclophosphamide 100 mg/kg (day -2) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in 31 patients with CD20+ non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Patients underwent dosimetry (day -21) with 5 mCi (185 MBq) 111In-ibritumomab tiuxetan following 250 mg/m2 rituximab, followed a week later by 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan to deliver a target dose of 1000 cGy to highest normal organ. Bone marrow biopsy was done on day -7 to estimate radiation dose and stem cells were reinfused when the radiation dose was estimated to be less than 5 cGy. The median 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan dose was 71.6 mCi (2649.2 MBq; range, 36.6-105 mCi; range, 1354.2-3885 MBq). Histology included follicular lymphoma (n = 12), diffuse large B-cell (n = 14), and mantle cell (n = 5). The median number of prior chemo-therapy treatments was 2. The treatment was well tolerated. The median times to reach an absolute neutrophil count greater than 500/microL and platelet count more than 20,000/microL were 10 days and 12 days, respectively. There were 2 deaths and 5 relapses. At a median follow-up of 22 months, the 2-year estimated overall survival and relapse-free survival rates are 92% and 78%, respectively. We conclude that high-dose 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan can be combined safely with high-dose etoposide and cyclophosphamide without an increase in transplant-related toxicity or delayed engraftment.
Figures
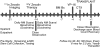

References
-
- Fisher RI, Gaynor ER, Dahlberg S, et al. Comparison of a standard regimen (CHOP) with three intensive chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;328: 1002-1006. - PubMed
-
- Vose JM, Anderson JR, Kessinger A, et al. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11: 1846-1851. - PubMed
-
- Nademanee A, Molina A, Dagis A, et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for poor-risk and relapsed intermediate-and high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma. 2000;1: 46-54. - PubMed
-
- Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemo-therapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333: 1540-1545. - PubMed
-
- Horning SJ, Negrin RS, Chao NJ, et al. Fractionated total-body irradiation, etoposide, and cyclophosphamide plus autografting in Hodgkin's disease and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12: 2552-2558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

