Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise
- PMID: 16002437
- PMCID: PMC1474228
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.093690
Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise
Abstract
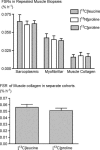
We hypothesized that an acute bout of strenuous, non-damaging exercise would increase rates of protein synthesis of collagen in tendon and skeletal muscle but these would be less than those of muscle myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins. Two groups (n = 8 and 6) of healthy young men were studied over 72 h after 1 h of one-legged kicking exercise at 67% of maximum workload (W(max)). To label tissue proteins in muscle and tendon primed, constant infusions of [1-(13)C]leucine or [1-(13)C]valine and flooding doses of [(15)N] or [(13)C]proline were given intravenously, with estimation of labelling in target proteins by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Patellar tendon and quadriceps biopsies were taken in exercised and rested legs at 6, 24, 42 or 48 and 72 h after exercise. The fractional synthetic rates of all proteins were elevated at 6 h and rose rapidly to peak at 24 h post exercise (tendon collagen (0.077% h(-1)), muscle collagen (0.054% h(-1)), myofibrillar protein (0.121% h(-1)), and sarcoplasmic protein (0.134% h(-1))). The rates decreased toward basal values by 72 h although rates of tendon collagen and myofibrillar protein synthesis remained elevated. There was no tissue damage of muscle visible on histological evaluation. Neither tissue microdialysate nor serum concentrations of IGF-I and IGF binding proteins (IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-4) or procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide changed from resting values. Thus, there is a rapid increase in collagen synthesis after strenuous exercise in human tendon and muscle. The similar time course of changes of protein synthetic rates in different cell types supports the idea of coordinated musculotendinous adaptation.
Figures


References
-
- Adams GR. Autocrine/paracrine IGF-I and skeletal muscle adaptation. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93:1159–1167. - PubMed
-
- Ahtikoski AM, Koskinen SO, Virtanen P, Kovanen V, Takala TE. Regulation of synthesis of fibrillar collagens in rat skeletal muscle during immobilization in shortened and lengthened positions. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001;172:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Atherton PJ, Babraj JA, Smith K, Singh J, Rennie MJ, Wackerhage H. Selective activation of AMPK-PGC-1α or PKB-TSC2-mTOR signaling can explain specific adaptive responses to endurance or resistance training-like electrical muscle stimulation. FASEB J. 2005;19:786–788. - PubMed
-
- Babraj J, Cuthbertson DJ, Rickhuss P, Meier-Augenstein W, Smith K, Bohé J, Wolfe RR, Gibson JN, Adams C, Rennie MJ. Sequential extracts of human bone show differing collagen synthetic rates. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:61–65. - PubMed
-
- Babraj JA, Cuthbertson DJR, Smith K, Langberg H, Miller BF, Krogsgaard MR, Kjaer M, Rennie MJ. Collagen synthesis in human musculoskeletal tissues and skin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005a 10.1152/ajpendo.00243.2005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

