Protein kinase C mediates up-regulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant, persistent Na+ current in rat and mouse sensory neurones
- PMID: 16002450
- PMCID: PMC1474230
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089771
Protein kinase C mediates up-regulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant, persistent Na+ current in rat and mouse sensory neurones
Abstract
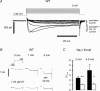
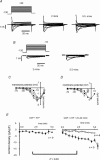
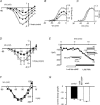
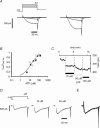
The tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-r) persistent Na(+) current, attributed to Na(V)1.9, was recorded in small (< 25 mum apparent diameter) dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurones cultured from P21 rats and from adult wild-type and Na(V)1.8 null mice. In conventional whole-cell recordings intracellular GTP-gamma-S caused current up-regulation, an effect inhibited by the PKC pseudosubstrate inhibitor, PKC19-36. The current amplitude was also up-regulated by 25 microM intracellular 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG) consistent with PKC involvement. In perforated-patch recordings, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) up-regulated the current, whereas membrane-permeant activators of protein kinase A (PKA) were without effect. PGE(2) did not acutely up-regulate the current. Conversely, both PGE(2) and PKA activation up-regulated the major TTX-r Na(+) current, Na(V)1.8. Extracellular ATP up-regulated the persistent current with an average apparent K(d) near 13 microM, possibly consistent with P2Y receptor activation. Numerical simulation of the up-regulation qualitatively reproduced changes in sensory neurone firing properties. The activation of PKC appears to be a necessary step in the GTP-dependent up-regulation of persistent Na(+) current.
Figures




References
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Baker MD, Bostock H. Low-threshold, persistent sodium current in rat large dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:1503–1513. - PubMed
-
- Baker MD, Wood JN. Involvement of Na+ channels in pain pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Waxman SG. Molecular identities of two tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in corneal axons. Exp Eye Res. 2002;75:193–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

