Sustained and transient covert attention enhance the signal via different contrast response functions
- PMID: 16005931
- PMCID: PMC1557421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2005.05.008
Sustained and transient covert attention enhance the signal via different contrast response functions
Abstract
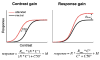
We investigated the mechanisms underlying the effects of sustained and transient covert attention on contrast sensitivity. The aim of this study was twofold: (1) Using a zero-noise display, we assessed whether sustained (endogenous) attention enhances contrast sensitivity via signal enhancement, and compared the magnitude of the effect with that of transient (exogenous) attention. (2) We compared the contrast psychometric functions for both sustained and transient attention and evaluated them in terms of contrast gain and response gain models. Observers performed a 2AFC orientation discrimination task on a tilted target Gabor, presented alone at 1 of 8 iso-eccentric locations. Either a neutral (baseline), peripheral (to manipulate transient attention), or a central cue (to manipulate sustained attention) preceded the target. Even in the absence of external noise, and using suprathreshold stimuli, observers showed an attentional effect, evidence in support of signal enhancement underlying both sustained and transient attention. Moreover, sustained attention caused a strictly leftward threshold shift in the psychometric function, supporting a contrast gain model. Interestingly, with transient attention we observed a change in asymptote in addition to a threshold shift. These findings suggest that whereas sustained attention operates strictly via contrast gain, transient attention may be better described by a mixture of response gain and contrast gain.
Figures



References
-
- Albrecht DG, Hamilton DB. Striate cortex of monkey and cat: Contrast response function. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1982;48(1):217–237. - PubMed
-
- Baldassi S, Burr DC. Feature-based integration of orientation signals in visual search. Vision Research. 2000;40:1293–1300. - PubMed
-
- Brainard DH. The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision. 1997;10:433–436. - PubMed
-
- Cameron EL, Tai JC, Carrasco M. Covert attention affects the psychometric function of contrast sensitivity. Vision Research. 2002;42:949–967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

