Identification of mast cell progenitors in adult mice
- PMID: 16006518
- PMCID: PMC1183570
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504197102
Identification of mast cell progenitors in adult mice
Abstract
It is well known that mast cells are derived from hematopoietic stem cells. However, in adult hematopoiesis, a committed mast cell progenitor has not yet been identified in any species, nor is it clear at what point during adult hematopoiesis commitment to the mast cell lineage occurs. We identified a cell population in adult mouse bone marrow, characterized as Lin(-)c-Kit(+)Sca-1(-)-Ly6c(-)FcepsilonRIalpha(-)CD27(-)beta7(+)T1/ST2+, that gives rise only to mast cells in culture and that can reconstitute the mast cell compartment when transferred into c-kit mutant mast cell-deficient mice. In addition, our experiments strongly suggest that these adult mast cell progenitors are derived directly from multipotential progenitors instead of, as previously proposed, common myeloid progenitors or granulocyte/macrophage progenitors.
Figures

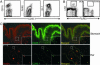
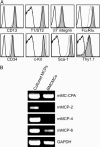
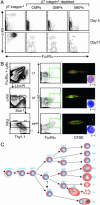
Comment in
-
Mast cell-committed progenitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 9;102(32):11129-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505073102. Epub 2005 Aug 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16061798 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kitamura, Y. (1989) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 7, 59-76. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe, D. D., Baram, D. & Mekori, Y. A. (1997) Physiol. Rev. 77, 1033-1079. - PubMed
-
- Kinet, J. P. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 931-972. - PubMed
-
- Galli, S. J., Kalesnikoff, J., Grimbaldeston, M. A., Piliponsky, A. M., Williams, C. M. M. & Tsai, M. (2005) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23, 749-786. - PubMed
-
- Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. (2002) Nature 420, 875-878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

