Influence of IL-6, COL1A1, and VDR gene polymorphisms on bone mineral density in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 16009674
- PMCID: PMC1774753
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.064212
Influence of IL-6, COL1A1, and VDR gene polymorphisms on bone mineral density in Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: Osteoporosis is an important cause of morbidity in patients with Crohn's disease. The pathogenesis of reduced bone mineral density (BMD) is multifactorial. A range of genetic factors have been implicated in other populations of patients with osteoporosis.
Aim: To investigate the influence of interleukin 6 (IL-6), collagen type 1alpha1 (COL1A1), and vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) on BMD in patients with Crohn's disease.
Patients: A cohort of 245 well characterised patients with Crohn's disease were recruited from the inflammatory bowel disease register at the Freeman Hospital and Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne, and the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK.
Methods: Patients were genotyped for IL-6 C-174G SNP, COL1A1 Sp1 binding site G T SNP, VDR Taq1, and Fok1 SNPs, and CARD15 R702W, G908R, and L1007fs SNPs. BMD was measured at the lumbar spine (LSP) and hip using dual energy x ray absorptiometry.
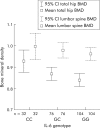
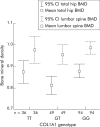
Results: A total of 158 female and 87 male patients, aged 24-70 years (mean 44), were recruited. There were no significant differences in the distribution of the tested SNPs when analysed for age, body mass index, pre/post-menopausal status, smoking, or steroid use. Two hundred and thirteen patients were genotyped for the IL-6 SNP. LSP and total hip BMD was significantly lower in patients with the GG genotype (48%) than the CC genotype (15%) (p = 0.041, p = 0.014). One hundred and eighty patients were genotyped for the COL1A1 SNP. There was no significant difference in BMD at LSP. Hip BMD was significantly lower in heterozygous patients compared with homozygous wild-types (p = 0.034). There were no significant differences in BMD between genotypes for the two VDR SNPs or the CARD15 genotypes examined.
Conclusion: IL-6 and COL1A1 gene polymorphisms influence BMD in patients with Crohn's disease but the particular VDR gene polymorphisms studied do not have a major effect.
Figures
References
-
- van Staa TP, Cooper C, Brusse LS, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and the risk of fracture. Gastroenterology 2003;125:1591–7. - PubMed
-
- Taylor BC, Schreiner PJ, Stone KL, et al. Long-term prediction of incident hip fracture risk in elderly white women: study of osteoporotic fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004;52:1479–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous