Chemoradiotherapy for colorectal cancer
- PMID: 16009693
- PMCID: PMC1774863
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.062745
Chemoradiotherapy for colorectal cancer
Figures




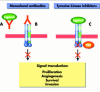

References
-
- Boyle P, Ferlay J. Cancer incidence and mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol 2005;16:481–8. - PubMed
-
- Russo MW, Wei JT, Thiny MT, et al. Digestive and liver diseases statistics, 2004. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1448–53. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
-
- Abulafi AM. Williams NSLocal recurrence of colorectal cancer: the problem, mechanisms, management and adjuvant therapy. Br J Surg 1994;81:7–19. - PubMed
-
- Faivre-Finn C, Bouvier AM, Mitry E, et al. Chemotherapy for colon cancer in a well-defined French population: is it under- or over-prescribed? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:353–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
