Palliative radiofrequency ablation for recurrent prostate cancer
- PMID: 16010507
- PMCID: PMC2386884
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-004-0200-8
Palliative radiofrequency ablation for recurrent prostate cancer
Abstract
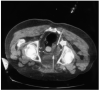
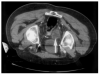
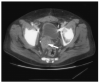
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive local therapy for cancer. Its efficacy is now becoming well documented in many different organs, including liver, kidney, and lung. The goal of RFA is typically complete eradication of a tumor in lieu of an invasive surgical procedure. However, RFA can also play an important role in the palliative care of cancer patients. Tumors which are surgically unresectable and incompatible for complete ablation present the opportunity for RFA to be used in a new paradigm. Cancer pain runs the gamut from minor discomfort relieved with mild pain medication to unrelenting suffering for the patient, poorly controlled by conventional means. RFA is a tool which can potentially palliate intractable cancer pain. We present here a case in which RFA provided pain relief in a patient with metastatic prostate cancer with pain uncontrolled by conventional methods.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CT-guided percutaneous minimally invasive radiofrequency ablation for the relief of cancer related pain from metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients: a retrospective study.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Feb;10(2):1494-1502. doi: 10.21037/apm-19-474. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33302633
-
Visceral and soft-tissue tumors: radiofrequency and alcohol ablation for pain relief--initial experience.Radiology. 2008 Sep;248(3):1067-76. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2483061883. Radiology. 2008. PMID: 18710995 Clinical Trial.
-
Palliation of soft tissue cancer pain with radiofrequency ablation.J Support Oncol. 2004 Sep-Oct;2(5):439-45. J Support Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15524075 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal hepatic metastases: Role of radiofrequency ablation.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2003 Mar;32(2):212-8. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2003. PMID: 12772525 Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation of malignant liver tumors.Ann Surg Oncol. 2003 May;10(4):338-47. doi: 10.1245/aso.2003.07.017. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12734080 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective palliative radiofrequency ablation for tumors causing pain, numbness and motor function disorders: case series.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Oct 28;7:765. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-765. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25348892 Free PMC article.
-
A long-term survivor of metastatic neuroendocrine prostate cancer treated with multimodal therapy: genetic consideration from next-generation sequencing.Int Cancer Conf J. 2021 Apr 13;10(3):174-180. doi: 10.1007/s13691-021-00482-2. eCollection 2021 Jul. Int Cancer Conf J. 2021. PMID: 34221827 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Local Ablative Therapies for the Treatment of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Cystic Lesions: A Review of the Current Literature.J Clin Med. 2023 May 7;12(9):3325. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093325. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37176764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preliminary experience in the management of brain and skull-base tumors with microwave ablation; feasibility guided by ultrasound, report from 23 cases.Surg Neurol Int. 2019 Feb 8;10:17. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_361_18. eCollection 2019. Surg Neurol Int. 2019. PMID: 31123624 Free PMC article.
-
Increased heating efficiency and selective thermal ablation of malignant tissue with DNA-encased multiwalled carbon nanotubes.ACS Nano. 2009 Sep 22;3(9):2667-73. doi: 10.1021/nn900368b. ACS Nano. 2009. PMID: 19655728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dupuy DE, Safran H, Mayo-Smith WW, Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastatic disease. Radiology. 1988;209(P):389.
-
- Wood BJ, Fojo A, Levy EB, Gomez-Horhez, Chang R, Spies J. Radiofrequency ablation of painful neoplasms as a palliative therapy: Early experience. Scientific Paper at the Society for Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology annual meeting; J Vasc Interv Radiol; 2000. p. 207.
-
- Goetz MP, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, et al. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: A multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:300–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

