LDL induces intracellular signalling and cell migration via atypical LDL-binding protein T-cadherin
- PMID: 16013438
- PMCID: PMC1282457
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-005-0250-5
LDL induces intracellular signalling and cell migration via atypical LDL-binding protein T-cadherin
Abstract
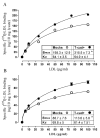
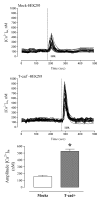
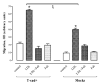
Cadherins are a superfamily of adhesion molecules that mediate Ca(2+)-dependent cell-cell adhesion. T-cadherin (T-cad), a unique glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored member of the cadherin superfamily, was initially identified by immunoblotting of vascular cell membranes as an atypical low affinity low density lipoprotein (LDL)-binding protein. It is not known whether this heterophilic interaction is physiologically relevant. Expression of T-cadherin is upregulated in vascular cells during atherosclerosis, restenosis and tumour angiogenesis, conditions characterized by enhanced cell migration and growth. Elevated levels of serum low density lipoproteins (LDL), which result in cholesterol accumulation in vascular wall, is a widely accepted risk factor in atherosclerosis development. Additionally to its metabolic effects, LDL can produce hormone-like effects in a number of cell types. This study has utilized HEK293 cells and L929 cells stably transfected with T-cadherin cDNA to investigate T-cad-dependent responses to LDL. Stable expression of T-cad in both HEK293 and L929 cells results in significantly (p < 0.05) elevated specific surface binding of [I125]-LDL. Compared with mock-transfectants, cells expressing T-cad exhibit significantly (p < 0.01) enhanced LDL-induced mobilization of intracellular Ca(2+)-stores and a significantly (p < 0.01) increased migration toward an LDL gradient (0.1% BSA + 60 microg/ml LDL) in Boyden chamber migration assay. Thus LDL-binding to T-cad is capable of activating physiologically relevant intracellular signaling and functional responses.
Figures
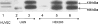


Similar articles
-
[Antiadhesive molecule T-cadherin is an atypical low-density lipoprotein receptor in vascular cells].Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2004 Aug;90(8):968-86. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2004. PMID: 15552364 Review. Russian.
-
LDL binds to surface-expressed human T-cadherin in transfected HEK293 cells and influences homophilic adhesive interactions.FEBS Lett. 1999 Dec 10;463(1-2):29-34. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01594-x. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10601632
-
Different spatiotemporal organization of GPI-anchored T-cadherin in response to low-density lipoprotein and adiponectin.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 Nov;1863(11):129414. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.129414. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019. PMID: 31404618
-
The glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor of human T-cadherin binds lipoproteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Oct 5;276(3):1240-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3465. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 11027617
-
A guide and guard: the many faces of T-cadherin.Cell Signal. 2009 Jul;21(7):1035-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.01.035. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19399994 Review.
Cited by
-
oxLDL promotes podocyte migration by regulating CXCL16, ADAM10 and ACTN4.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):1976-1984. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11292. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32705248 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Factors for Coronary Heart Disease and Their Mechanisms: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review of Common Variants from Genome-Wide Association Studies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;12(10):2561. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102561. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of T-cadherin in NSCLC.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 19;9:207-16. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74259. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25565774 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of rare missense variants of human CDH13 found in adult attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) patients.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 1;8(8):e71445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071445. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936508 Free PMC article.
-
T-cadherin is essential for adiponectin-mediated revascularization.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24886-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454835. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23824191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perez-Moreno M, Jamora C, Fuchs E. Sticky business: Orchestrating cellular signals at adherens junctions. Cell. 2003;112:535–548. - PubMed
-
- Angst BD, Marcozzi C, Magee AI. The cadherin superfamily: Diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:629–641. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov DB, Philippova MP, Tkachuk VA. Structure and functions of classical cadherins. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2001;66:1174–1186. - PubMed
-
- Ranscht B, Dours-Zimmermann MT. T-cadherin, a novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule in the nervous system lacks the conserved cytoplasmic region. Neuron. 1991;7:391–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

