Suppression of myasthenogenic responses of a T cell line by a dual altered peptide ligand by induction of CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells
- PMID: 16014414
- PMCID: PMC1177416
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504578102
Suppression of myasthenogenic responses of a T cell line by a dual altered peptide ligand by induction of CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 23;102(34):12288
Abstract
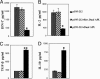
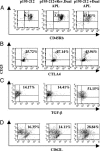
Myasthenia gravis is a T cell-dependent, antibody-mediated autoimmune disease. A dual altered peptide ligand (APL) that is composed of the tandemly arranged two single amino acid analogs of two myasthenogenic peptides, p195-212 and p259-271, was demonstrated to down-regulate in vitro and in vivo myasthenia gravis-associated autoreactive responses. The aims of this study were to demonstrate the suppressive properties and to elucidate the mechanism of action of the dual APL on a T cell line specific to the myasthenogenic peptide p195-212. We demonstrate here that incubation of cells of the line with the dual APL resulted in the inhibition of proliferation and secretion of IL-2 and IFN-gamma triggered by p195-212. In contrast, secretion of TGF-beta and IL-10 was upregulated. The dual APL induced the generation of CD4+CD25+ cells that were characterized by the expression of CD45Rb(low), cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4, TGF-beta, CD62L, Foxp3, and neuropilin. In addition, the dual APL-treated cells were capable of inhibiting the proliferation response of the line when the two sets of cells were cocultured. The role of CD4+CD25+ cells was further confirmed by demonstrating that the suppression was abrogated by blocking/neutralization of CD25. Thus, the dual APL acts by inducing the formation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells. By using a T cell line, we could show that the immunosuppressive CD4+CD25+ cells were indeed induced by the dual APL and are not part of the naturally occurring regulatory cells.
Figures



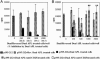
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

