T-bet is required for optimal proinflammatory CD4+ T-cell trafficking
- PMID: 16014561
- PMCID: PMC1895048
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1393
T-bet is required for optimal proinflammatory CD4+ T-cell trafficking
Abstract
Inflammatory responses are controlled by T helper 1 (Th1) lymphocytes. An important function of this polarity is the ability of T cells to traffick appropriately in vivo. This differential trafficking is dependent upon the binding of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 to P- and E-selectin on inflamed endothelium as well as the expression of specific chemokine receptors. Here we show that in the absence of T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet), selective migration of T cells in vivo is completely abrogated and that T-bet regulates the binding of CD4(+) T cells to P-selectin. T-bet is also required for the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Thus, T-bet controls Th1-cell migration to inflammatory sites, which has fundamental consequences for the control of immunologic disease.
Figures
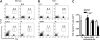
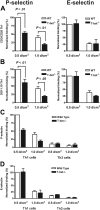
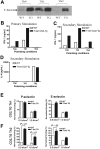
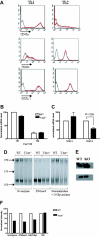
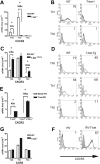
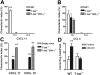
 , T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–.(B) Chemotactic response to CCL4 (MIP-1β, 10 nM). □ indicates WT; ▪, T-bet–/–;
, T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–.(B) Chemotactic response to CCL4 (MIP-1β, 10 nM). □ indicates WT; ▪, T-bet–/–;  , T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–. (C) Chemotaxis of retrovirally transduced T-bet (or empty vector control) into T-bet–/– and T-bet–/– × IFN-γ–/– T cells to CXCR3 ligands, CXCL11 (100 nM), and CXCL10 (IP-10, 100 nM). □ indicates empty virus; ▪, T-bet–/–;
, T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–. (C) Chemotaxis of retrovirally transduced T-bet (or empty vector control) into T-bet–/– and T-bet–/– × IFN-γ–/– T cells to CXCR3 ligands, CXCL11 (100 nM), and CXCL10 (IP-10, 100 nM). □ indicates empty virus; ▪, T-bet–/–;  , T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–. (D) Attachment of WT and T-bet–/– T cells to unstimulated endothelial cells under shear flow in the absence or presence of CXCL10 (40 ng/mL) (mean ± SEM). □ indicates control; ▪, CXCL10. **P < .05.
, T-bet–/–/IFN-γ–/–. (D) Attachment of WT and T-bet–/– T cells to unstimulated endothelial cells under shear flow in the absence or presence of CXCL10 (40 ng/mL) (mean ± SEM). □ indicates control; ▪, CXCL10. **P < .05.References
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383: 787-793. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Peng SL, Glimcher LH. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Ann Rev Immunol. 2003;21: 713-758. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman GC, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000;100: 655-669. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Stemmann C, Satoskar AR, Sleckman BP, Glimcher LH. Distinct effects of T-bet in TH1 lineage commitment and IFN-gamma production in CD4 and CD8 T cells. Science. 2002;295: 338-342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

