MDM2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy
- PMID: 16014563
- PMCID: PMC1895324
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0553
MDM2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy
Abstract
Although TP53 mutations are rare in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), inactivation of wild-type p53 protein frequently occurs through overexpression of its negative regulator MDM2 (murine double minute 2). Recently, small-molecule antagonists of MDM2, Nutlins, have been developed that inhibit the p53-MDM2 interaction and activate p53 signaling. Here, we study the effects of p53 activation by Nutlin-3 in AML cells. Treatment with MDM2 inhibitor triggered several molecular events consistent with induction of apoptosis: loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, caspase activation, phosphatidylserine externalization, and DNA fragmentation. There was a positive correlation in primary AML samples with wild-type p53 between baseline MDM2 protein levels and apoptosis induced by MDM2 inhibition. No induction of apoptosis was observed in AML samples harboring mutant p53. Colony formation of AML progenitors was inhibited in a dose-dependent fashion, whereas normal CD34+ progenitor cells were less affected. Mechanistic studies suggested that Nutlin-induced apoptosis was mediated by both transcriptional activation of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, and transcription-independent mitochondrial permeabilization resulting from mitochondrial p53 translocation. MDM2 inhibition synergistically enhanced cytotoxicity of cytosine arabinoside and doxorubicin in AML blasts but not in normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. p53 activation by targeting the p53-MDM2 interaction might offer a novel therapeutic strategy for AML that retain wild-type p53.
Figures
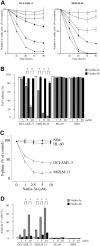

 ) for 72 hours, and the annexin V–positive fractions were measured by flow cytometry. □ represents DMSO-treated controls. (B) Primary AML cells from patient 8 were treated with the indicated concentrations of Nutlin-3a, and flow cytometry analysis using CD34-PE and annexin V–FITC antibodies was performed at the indicated times.
) for 72 hours, and the annexin V–positive fractions were measured by flow cytometry. □ represents DMSO-treated controls. (B) Primary AML cells from patient 8 were treated with the indicated concentrations of Nutlin-3a, and flow cytometry analysis using CD34-PE and annexin V–FITC antibodies was performed at the indicated times.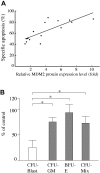

 ), 10 μM Nutlin-3a (
), 10 μM Nutlin-3a ( ), or a combination of cycloheximide and Nutlin-3a (▪). Δψm was assessed by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as mean ± SD of triplicate measurements. Comparable results were obtained in 2 other independent experiments. *P < .05.
), or a combination of cycloheximide and Nutlin-3a (▪). Δψm was assessed by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as mean ± SD of triplicate measurements. Comparable results were obtained in 2 other independent experiments. *P < .05.
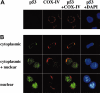
References
-
- Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000;408: 307-310. - PubMed
-
- Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991;253: 49-53. - PubMed
-
- Bykov VJ, Wiman KG. Novel cancer therapy by reactivation of the p53 apoptosis pathway. Ann Med. 2003;35: 458-465. - PubMed
-
- Harris CC. Structure and function of the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues for rational cancer therapeutic strategies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88: 1442-1455. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993;74: 957-967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

