PAK5 kinase is an inhibitor of MARK/Par-1, which leads to stable microtubules and dynamic actin
- PMID: 16014608
- PMCID: PMC1196348
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0081
PAK5 kinase is an inhibitor of MARK/Par-1, which leads to stable microtubules and dynamic actin
Abstract
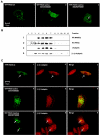
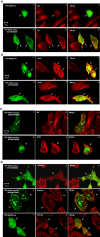
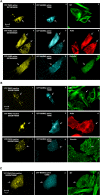
MARK/Par-1 is a kinase involved in development of embryonic polarity. In neurons, MARK phosphorylates tau protein and causes its detachment from microtubules, the tracks of axonal transport. Because the target sites of MARK on tau occur at an early stage of Alzheimer neurodegeneration, we searched for interaction partners of MARK. Here we report that MARK2 is negatively regulated by PAK5, a neuronal member of the p21-activated kinase family. PAK5 suppresses the activity of MARK2 toward its target, tau protein. The inhibition requires the binding between the PAK5 and MARK2 catalytic domains, but does not require phosphorylation. In transfected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells both kinases show a vesicular distribution with partial colocalization on endosomes containing AP-1/2. Although MARK2 transfected alone destabilizes microtubules and stabilizes actin stress fibers, PAK5 keeps microtubules stable through the down-regulation of MARK2 but destabilizes the F-actin network so that stress fibers and focal adhesions disappear and cells develop filopodia. The results point to an inverse relationship between actin- and microtubule-related signaling by the PAK5 and MARK2 pathways that affect both cytoskeletal networks.
Figures




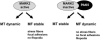
Similar articles
-
Signaling from MARK to tau: regulation, cytoskeletal crosstalk, and pathological phosphorylation.Neurodegener Dis. 2006;3(4-5):207-17. doi: 10.1159/000095258. Neurodegener Dis. 2006. PMID: 17047359
-
Phosphorylation of MAP2c and MAP4 by MARK kinases leads to the destabilization of microtubules in cells.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1999 Nov;44(3):209-24. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(199911)44:3<209::AID-CM6>3.0.CO;2-4. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1999. PMID: 10542369
-
Spred1 and TESK1--two new interaction partners of the kinase MARKK/TAO1 that link the microtubule and actin cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Apr;19(4):1391-403. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0730. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18216281 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of polarity-inducing kinase family MARK/Par-1 within the branch of AMPK/Snf1-related kinases.FASEB J. 2010 Jun;24(6):1637-48. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-148064. Epub 2010 Jan 13. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20071654 Review.
-
PAR-1/MARK: a kinase essential for maintaining the dynamic state of microtubules.Cell Struct Funct. 2012;37(1):21-5. doi: 10.1247/csf.11038. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Cell Struct Funct. 2012. PMID: 22139392 Review.
Cited by
-
The overexpression of P21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) promotes paclitaxel-chemoresistance of epithelial ovarian cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Nov;383(1-2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1767-7. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23877225
-
Regulation of glucose homeostasis by KSR1 and MARK2.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029304. Epub 2011 Dec 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22206009 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule affinity-regulating kinases are potential druggable targets for Alzheimer's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Nov;74(22):4159-4169. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2574-1. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28634681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 functions downstream of the PAR-3/PAR-6/atypical PKC complex in regulating hippocampal neuronal polarity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 30;103(22):8534-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509955103. Epub 2006 May 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16717194 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic effects of doublecortin and MARK2/Par-1 in the developing cerebral cortex.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):13008-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2363-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustinack, J. C., Schneider, A., Mandelkow, E.-M., and Hyman, B. (2002). Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 103, 26-35. - PubMed
-
- Benton, R., Palacios, I. M., St. Johnston, D. (2002). Drosophila 14-3-3/PAR-5 is an essential mediator of PAR-1 function in axis formation. Dev. Cell 3, 659-671. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch, G. M. (2003). Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 743-781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

