The zebrafish shocked gene encodes a glycine transporter and is essential for the function of early neural circuits in the CNS
- PMID: 16014722
- PMCID: PMC6725421
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5009-04.2005
The zebrafish shocked gene encodes a glycine transporter and is essential for the function of early neural circuits in the CNS
Abstract
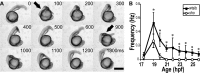
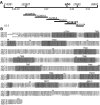
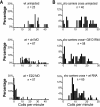
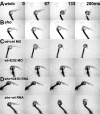
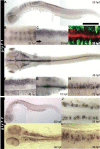
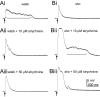
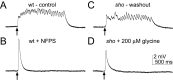
shocked (sho) is a zebrafish mutation that causes motor deficits attributable to CNS defects during the first2dof development. Mutant embryos display reduced spontaneous coiling of the trunk, diminished escape responses when touched, and an absence of swimming. A missense mutation in the slc6a9 gene that encodes a glycine transporter (GlyT1) was identified as the cause of the sho phenotype. Antisense knock-down of GlyT1 in wild-type embryos phenocopies sho, and injection of wild-type GlyT1 mRNA into mutants rescues them. A comparison of glycine-evoked inward currents in Xenopus oocytes expressing either the wild-type or mutant protein found that the missense mutation results in a nonfunctional transporter. glyt1 and the related glyt2 mRNAs are expressed in the hindbrain and spinal cord in nonoverlapping patterns. The fact that these regions are known to be required for generation of early locomotory behaviors suggests that the regulation of extracellular glycine levels in the CNS is important for proper function of neural networks. Furthermore, physiological analysis after manipulation of glycinergic activity in wild-type and sho embryos suggests that the mutant phenotype is attributable to elevated extracellular glycine within the CNS.
Figures
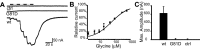
Similar articles
-
Synaptic homeostasis in a zebrafish glial glycine transporter mutant.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Oct;100(4):1716-23. doi: 10.1152/jn.90596.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 20. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18715895 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of glycinergic neurons in the brain of glycine transporter-2 transgenic Tg(glyt2:Gfp) adult zebrafish: relationship to brain-spinal descending systems.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Feb 1;521(2):389-425. doi: 10.1002/cne.23179. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 22736487
-
Transport activities and expression patterns of glycine transporters 1 and 2 in the developing murine brain stem and spinal cord.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jul 13;423(4):661-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22695116
-
Functional 'glial' GLYT1 glycine transporters expressed in neurons.J Neurochem. 2010 Aug;114(3):647-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06802.x. Epub 2010 May 6. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20477934 Review.
-
Glycine transporters: essential regulators of synaptic transmission.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):55-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0340055. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16417482 Review.
Cited by
-
Using imaging and genetics in zebrafish to study developing spinal circuits in vivo.Dev Neurobiol. 2008 May;68(6):817-34. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20617. Dev Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18383546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired glycine neurotransmission causes adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.J Clin Invest. 2024 Jan 16;134(2):e168783. doi: 10.1172/JCI168783. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 37962965 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Conservation and Genetic Divergence of Chordate Glycinergic Neurotransmission: Insights from Amphioxus Glycine Transporters.Cells. 2021 Dec 2;10(12):3392. doi: 10.3390/cells10123392. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943900 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Measurement of Glycine Receptor Turnover and Synaptic Size Reveals Differences between Functional Classes of Motoneurons in Zebrafish.Curr Biol. 2017 Apr 24;27(8):1173-1183. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.032. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Curr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28416115 Free PMC article.
-
Na(v)1.6a is required for normal activation of motor circuits normally excited by tactile stimulation.Dev Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;70(7):508-22. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20791. Dev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20225246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Applegarth DA, Toone JR (2004) Glycine encephalopathy (nonketotic hyperglycinaemia): review and update. J Inherit Metab Dis 27: 417-422. - PubMed
-
- Aragon C, Lopez-Corcuera B (2003) Structure, function and regulation of glycine neurotransporters. Eur J Pharmacol 479: 249-262. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y (2001) Developing networks play a similar melody. Trends Neurosci 24: 353-360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
