Variant-specific tropism of human herpesvirus 6 in human astrocytes
- PMID: 16014907
- PMCID: PMC1181567
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9439-9448.2005
Variant-specific tropism of human herpesvirus 6 in human astrocytes
Abstract
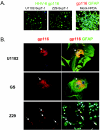
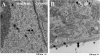
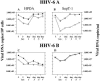
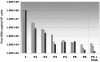
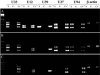
Though first described as a lymphotropic virus, human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is highly neuropathogenic. Two viral variants are known: HHV-6A and HHV-6B. Both variants can infect glial cells and have been differentially associated with central nervous system diseases, suggesting an HHV-6 variant-specific tropism for glial cell subtypes. We have performed infections with both viral variants in human progenitor-derived astrocytes (HPDA) and monitored infected cell cultures for cytopathic effect (CPE), intra- and extracellular viral DNA load, the presence of viral particles by electronic microscopy, mRNA transcription, and viral protein expression. HHV-6A established a productive infection with CPE, visible intracellular virions, and high virus DNA loads. HHV-6B-infected HPDA showed no morphological changes, intracellular viral particles, and decreasing intra- and extracellular viral DNA over time. After long-term passage, HHV-6B-infected HPDA had stable but low levels of intracellular viral DNA load with no detectable viral mRNA. Our results demonstrate that HHV-6A and HHV-6B have differential tropisms and patterns of infection for HPDA in vitro, where HHV-6A results in a productive lytic infection. In contrast, HHV-6B was associated with a nonproductive infection. These findings suggest that HHV-6 variants might be responsible for specific infection patterns in glial cells in vivo. Astrocytes may be an important reservoir for this virus in which differential tropism of HHV-6A and HHV-6B may be associated with different disease outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Ablashi, D. V., N. Balachandran, S. F. Josephs, C. L. Hung, G. R. Krueger, B. Kramarsky, S. Z. Salahuddin, and R. C. Gallo. 1991. Genomic polymorphism, growth properties, and immunologic variations in human herpesvirus-6 isolates. Virology 184:545-552. - PubMed
-
- Akhyani, N., R. Berti, M. B. Brennan, S. S. Soldan, J. M. Eaton, H. F. McFarland, and S. Jacobson. 2000. Tissue distribution and variant characterization of human herpesvirus (HHV)-6: increased prevalence of HHV-6A in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Infect. Dis. 182:1321-1325. - PubMed
-
- Albright, A. V., E. Lavi, J. B. Black, S. Goldberg, M. J. O'Connor, and F. Gonzalez-Scarano. 1998. The effect of human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) on cultured human neural cells: oligodendrocytes and microglia. J. Neurovirol. 4:486-494. - PubMed
-
- Araque, A., G. Carmignoto, and P. G. Haydon. 2001. Dynamic signaling between astrocytes and neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63:795-813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

