Two Sp1/Sp3 binding sites in the major immediate-early proximal enhancer of human cytomegalovirus have a significant role in viral replication
- PMID: 16014922
- PMCID: PMC1181558
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9597-9607.2005
Two Sp1/Sp3 binding sites in the major immediate-early proximal enhancer of human cytomegalovirus have a significant role in viral replication
Abstract
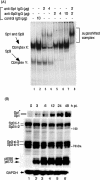
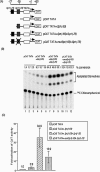
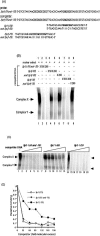
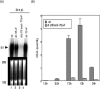
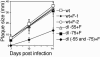
We previously demonstrated that the major immediate early (MIE) proximal enhancer containing one GC box and the TATA box containing promoter are minimal elements required for transcription and viral replication in human fibroblast cells (H. Isomura, T. Tsurumi, M. F. Stinski, J. Virol. 78:12788-12799, 2004). After infection, the level of Sp1 increased while Sp3 remained constant. Here we report that either Sp1 or Sp3 transcription factors bind to the GC boxes located at approximately positions -55 and -75 relative to the transcription start site (+1). Both the Sp1 and Sp3 binding sites have a positive and synergistic effect on the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) major immediate-early (MIE) promoter. There was little to no change in MIE transcription or viral replication for recombinant viruses with one or the other Sp1 or Sp3 binding site mutated. In contrast, mutation of both the Sp1 and Sp3 binding sites caused inefficient MIE transcription and viral replication. These data indicate that the Sp1 and Sp3 binding sites have a significant role in HCMV replication in human fibroblast cells.
Figures


References
-
- Aoyama, T., T. Okamoto, S. Nagayama, K. Nishijo, T. Ishibe, K. Yasura, T. Nakayama, T. Nakamura, and J. Toguchida. 2004. Methylation in the core-promoter region of the chondromodulin-I gene determines the cell-specific expression by regulating the binding of transcriptional activator Sp3. J. Biol. Chem. 279:28789-28797. - PubMed
-
- Apt, D., R. M. Watts, G. Suske, and H. U. Bernard. 1996. High Sp1/Sp3 ratios in epithelial cells during epithelial differentiation and cellular transformation correlate with the activation of the HPV-16 promoter. Virology 224:281-291. - PubMed
-
- Boekhoudt, G. H., Z. Guo, G. W. Beresford, and J. M. Boss. 2003. Communication between NF-κB and Sp1 controls histone acetylation within the proximal promoter of the monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene. J. Immunol. 170:4139-4147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

