Hepatitis C virus stimulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 via oxidative stress: role of prostaglandin E2 in RNA replication
- PMID: 16014934
- PMCID: PMC1181604
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9725-9734.2005
Hepatitis C virus stimulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 via oxidative stress: role of prostaglandin E2 in RNA replication
Retraction in
-
Retraction for Waris and Siddiqui, "Hepatitis C Virus Stimulates the Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 via Oxidative Stress: Role of Prostaglandin E2 in RNA Replication".J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e01402-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01402-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32934070 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
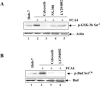
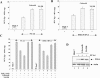
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major cause of chronic liver disease, which can lead to the development of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recently, the activation of cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) has been implicated in the HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. In this study, we focus on the signaling pathway leading to Cox-2 activation induced by HCV gene expression. Here, we demonstrate that the HCV-induced reactive oxygen species and subsequent activation of NF-kappaB mediate the activation of Cox-2. The HCV-induced Cox-2 was sensitive to antioxidant (pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate), Ca(2+) chelator (BAPTA-AM), and calpain inhibitor (N-acetyl-Leu-Leu-Met-H). The levels of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)), the product of Cox-2 activity, are increased in HCV-expressing cells. Furthermore, HCV-expressing cells treated with the inhibitors of Cox-2 (celecoxib and NS-398) showed significant reduction in PGE(2) levels. We also observed the enhanced phosphorylation of Akt and its downstream substrates glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and proapoptotic Bad in the HCV replicon-expressing cells. These phosphorylation events were sensitive to inhibitors of Cox-2 (celecoxib and NS-398) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (LY294002). Our results also suggest a potential role of Cox-2 and PGE(2) in HCV RNA replication. These studies provide insight into the mechanisms by which HCV induces intracellular events relevant to liver pathogenesis associated with viral infection.
Figures





References
-
- Bae, S. H., E. S. Jung, Y. M. Park, B. S. Kim, B. K. Kim, D. G. Kim, and W. S. Ryu. 2001. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a Cox-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clin. Cancer Res. 7:1410-1418. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, S. B., S. Eligini, M. Brambilla, E. Tremoli, and S. Colli. 2003. Reactive oxygen species mediate cyclooxygenase-2 induction during monocyte to macrophage differentiation: critical role of NADPH oxidase. Cardiovasc. Res. 60:187-197. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R., and V. Lohmann. 2000. Replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Gen. Virol. 81:1631-1648. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R., and V. Lohmann. 2001. Novel cell culture systems for the hepatitis C virus. Antiviral Res. 52:1-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

