A virus essential for insect host-parasite interactions encodes cystatins
- PMID: 16014938
- PMCID: PMC1181612
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9765-9776.2005
A virus essential for insect host-parasite interactions encodes cystatins
Abstract
Cotesia congregata is a parasitoid wasp that injects its eggs in the host caterpillar Manduca sexta. In this host-parasite interaction, successful parasitism is ensured by a third partner: a bracovirus. The relationship between parasitic wasps and bracoviruses constitutes one of the few known mutualisms between viruses and eukaryotes. The C. congregata bracovirus (CcBV) is injected at the same time as the wasp eggs in the host hemolymph. Expression of viral genes alters the caterpillar's immune defense responses and developmental program, resulting in the creation of a favorable environment for the survival and emergence of adult parasitoid wasps. Here, we describe the characterization of a CcBV multigene family which is highly expressed during parasitism and which encodes three proteins with homology to members of the cystatin superfamily. Cystatins are tightly binding, reversible inhibitors of cysteine proteases. Other cysteine protease inhibitors have been described for lepidopteran viruses; however, this is the first description of the presence of cystatins in a viral genome. The expression and purification of a recombinant form of one of the CcBV cystatins, cystatin 1, revealed that this viral cystatin is functional having potent inhibitory activity towards the cysteine proteases papain, human cathepsins L and B and Sarcophaga cathepsin B in assays in vitro. CcBV cystatins are, therefore, likely to play a role in host caterpillar physiological deregulation by inhibiting host target proteases in the course of the host-parasite interaction.
Figures

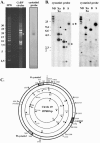




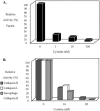
References
-
- Abe, K., Y. Emori, H. Kondo, K. Suzuki, and S. Arai.c 1987. Molecular cloning of a cysteine proteinase inhibitor of rice (oryzacystatin). Homology with animal cystatins and transient expression in the ripening process of rice seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 262:16793-16797. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson, M., M. Alvarez-Fernandez, and C. M. Nathanson. 2003. Cystatins. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2003:179-199. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht, U., T. Wyler, R. Pfister-Wilhelm, A. Gruber, P. Stettler, P. Heiniger, F. Kurt, D. Schümperli, and B. Lanzrein. 1994. Polydnavirus of the parasitic wasp Chelonus inanitus (Braconidae): characterization, genome organization and time point of replication. J. Gen. Virol. 75:3353-3363. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

