Diversity, divergence, and evolution of cell-free human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vaginal secretions and blood of chronically infected women: associations with immune status
- PMID: 16014941
- PMCID: PMC1181596
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9799-9809.2005
Diversity, divergence, and evolution of cell-free human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vaginal secretions and blood of chronically infected women: associations with immune status
Abstract
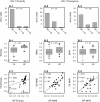
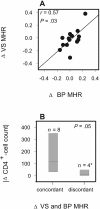
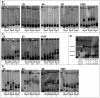
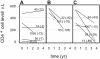
Most human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infections are believed to be the result of exposure to the virus in genital secretions. However, prevention and therapeutic strategies are usually based on characterizations of HIV-1 in blood. To understand better the dynamics between HIV-1 quasispecies in the genital tract and blood, we performed heteroduplex assays on amplified env products from cell-free viral RNA in paired vaginal secretion (VS) and blood plasma (BP) samples of 14 women followed for 1.5 to 3.5 years. Diversity and divergence were less in VS than in BP (P = 0.03 and P < 0.01, respectively), and divergence at both sites was correlated with blood CD4(+) cell levels (VS, P = 0.05; BP, P = 0.01). Evolution of quasispecies was observed in 58% of the women; the loss or gain of quasispecies in VS or BP was always accompanied by such changes at the other site. In addition, sustained compartmentalization of quasispecies in VS was found for four women, even as CD4(+) cell levels decreased to low levels (<50 cells/microl). Quasispecies changes over time were associated with fluctuations in CD4(+) cell levels; concordant increases or decreases in VS and BP divergence had greater CD4(+) cell level changes than intervals with discordant changes (P = 0.05), and women with evolving quasispecies had greater decreases in CD4(+) cell levels compared to that for women who maintained the same quasispecies (P < 0.05). Thus, diversity, divergence, and evolution of cell-free HIV-1 in VS can be different from that in BP, and dynamics between their respective quasispecies are associated with changes in CD4(+) cell levels.
Figures


References
-
- Albert, J., B. Abrahamsson, K. Nagy, E. Aurelius, H. Gaines, G. Nystrom, and E. M. Fenyo. 1990. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS 4:107-112. - PubMed
-
- Altfeld, M., E. S. Rosenberg, R. Shankarappa, J. S. Mukherjee, F. M. Hecht, R. L. Eldridge, M. M. Addo, S. H. Poon, M. N. Phillips, G. K. Robbins, P. E. Sax, S. Boswell, J. O. Kahn, C. Brander, P. J. R. Goulder, J. A. Levy, J. I. Mullins, and B. D. Walker. 2001. Cellular immune responses and viral diversity in individuals treated during acute and early HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 193:169-180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arendrup, M., C. Nielsen, J.-E. S. Hansen, C. Pedersen, L. Mathiesen, and J. O. Nielsen. 1992. Autologous HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies: emergence of neutralization-resistant escape virus and subsequent development of escape virus neutralizing antibodies. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 5:303-307. - PubMed
-
- Artenstein, A. W., T. C. VanCott, K. V. Sitz, M. L. Robb, K. F. Wagner, S. C. D. Veit, A. F. Rogers, R. P. Garner, J. W. Byron, P. R. Burnett, and D. L. Birx. 1997. Mucosal immune responses in four distinct compartments of women infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: a comparison by site and correlation with clinical information. J. Infect. Dis. 175:265-271. - PubMed
-
- Belec, L., T. Dupre, T. Prazuck, C. Tevi-Benissan, J.-M. Kanga, O. Pathey, X.-S. Lu, and J. Pillot. 1995. Cervicovaginal overproduction of specific IgG to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) contrasts with normal or impaired IgA local response in HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 172:691-697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

