The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3a protein up-regulates expression of fibrinogen in lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 16014971
- PMCID: PMC1181587
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.10083-10087.2005
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3a protein up-regulates expression of fibrinogen in lung epithelial cells
Abstract
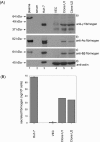
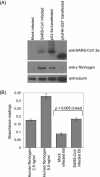
Here we analyzed the gene expression profile of cells that stably express the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3a protein to determine its effects on host functions. A lung epithelial cell-line, A549, was chosen for this study because the lung is the primary organ infected by SARS-CoV and fatalities resulted mainly from pulmonary complications. Our results showed that the expression of 3a up-regulates the mRNA levels of all three subunits, Aalpha, Bbeta, and gamma, of fibrinogen. Consequently, the intracellular levels as well as the secretion of fibrinogen were increased. We also observed increased fibrinogen levels in SARS-CoV-infected Vero E6 cells.
Figures
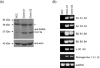
References
-
- Bini, A., P. J. Simpson-Haidaris, and B. J. Kudryk. 2000. Fibrin/fibrinogen, p. 372. In A. Bikfalvi (ed.), Encyclopedic reference of vascular biology & pathology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
-
- Chong, P. Y., P. Chui, A. E. Ling, T. J. Franks, D. Y. Tai, Y. S. Leo, G. J. Kaw, G. Wansaicheong, K. P. Chan, L. L. Ean Oon, E. S. Teo, K. B. Tan, N. Nakajima, T. Sata, and W. D. Travis. 2004. Analysis of deaths during the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) epidemic in Singapore: challenges in determining a SARS diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 128:195-204. - PubMed
-
- Clark, R. A. F. 1996. Wound repair, p. 617. In R. A. F. Clark (ed.), The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Dowton, S. B., and H. R. Colten. 1988. Acute phase reactants in inflammation and infection. Semin. Hematol. 25:84-90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

