TAF4 inactivation in embryonic fibroblasts activates TGF beta signalling and autocrine growth
- PMID: 16015375
- PMCID: PMC1182243
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600748
TAF4 inactivation in embryonic fibroblasts activates TGF beta signalling and autocrine growth
Abstract
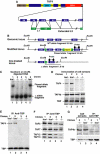
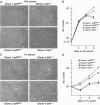
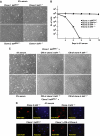
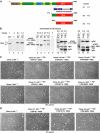
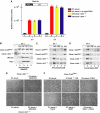
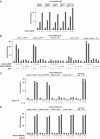
We have inactivated transcription factor TFIID subunit TBP-associated factor 4 (TAF4) in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Mutant taf4(-/-) cells are viable and contain intact TFIID comprising the related TAF4b showing that TAF4 is not an essential protein. TAF4 inactivation deregulates more than 1000 genes indicating that TFIID complexes containing TAF4 and TAF4b have distinct target gene specificities. However, taf4(-/-) cell lines have altered morphology and exhibit serum-independent autocrine growth correlated with the induced expression of several secreted mitotic factors and activators of the transforming growth factor beta signalling pathway. In addition to TAF4 inactivation, many of these genes can also be induced by overexpression of TAF4b. A competitive equilibrium between TAF4 and TAF4b therefore regulates expression of genes controlling cell proliferation. We have further identified a set of genes that are regulated both by TAF4 and upon adaptation to serum starvation and which may be important downstream mediators of serum-independent growth. Our study also shows that TAF4 is an essential cofactor for activation by the retinoic acid receptor and CREB, but not for Sp1 and the vitamin D3 receptor.
Figures



References
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB (2003) Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci 116: 217–224 - PubMed
-
- Brand M, Yamamoto K, Staub A, Tora L (1999) Identification of TATA-binding protein-free TAFII-containing complex subunits suggests a role in nucleosome acetylation and signal transduction. J Biol Chem 274: 18285–18289 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

