Characterization of 17alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity (17alpha-HSD) and its involvement in the biosynthesis of epitestosterone
- PMID: 16018803
- PMCID: PMC1185520
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-6-12
Characterization of 17alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity (17alpha-HSD) and its involvement in the biosynthesis of epitestosterone
Abstract
Background: Epi-testosterone (epiT) is the 17alpha-epimer of testosterone. It has been found at similar level as testosterone in human biological fluids. This steroid has thus been used as a natural internal standard for assessing testosterone abuse in sports. EpiT has been also shown to accumulate in mammary cyst fluid and in human prostate. It was found to possess antiandrogenic activity as well as neuroprotective effects. So far, the exact pathway leading to the formation of epiT has not been elucidated.
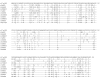
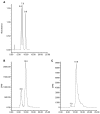
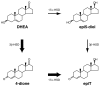
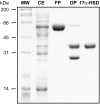
Results: In this report, we describe the isolation and characterization of the enzyme 17alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. The name is given according to its most potent activity. Using cells stably expressing the enzyme, we show that 17alpha-HSD catalyzes efficienty the transformation of 4-androstenedione (4-dione), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), 5alpha-androstane-3,17-dione (5alpha-dione) and androsterone (ADT) into their corresponding 17alpha-hydroxy-steroids : epiT, 5-androstene-3beta,17alpha-diol (epi5diol), 5alpha-androstane-17alpha-ol-3-one (epiDHT) and 5alpha-androstane-3alpha,17alpha-diol (epi3alpha-diol), respectively. Similar to other members of the aldo-keto reductase family that possess the ability to reduce the keto-group into hydroxyl-group at different position on the steroid nucleus, 17alpha-HSD could also catalyze the transformation of DHT, 5alpha-dione, and 5alpha-pregnane-3,20-dione (DHP) into 3alpha-diol, ADT and 5alpha-pregnane-3alpha-ol-20-one (allopregnanolone) through its less potent 3alpha-HSD activity. We also have over-expressed the 17alpha-HSD in Escherichia coli and have purified it by affinity chromatography. The purified enzyme exhibits the same catalytic properties that have been observed with cultured HEK-293 stably transfected cells. Using quantitative Realtime-PCR to study tissue distribution of this enzyme in the mouse, we observed that it is expressed at very high levels in the kidney.
Conclusion: The present study permits to clarify the biosynthesis pathway of epiT. It also offers the opportunity to study gene regulation and function of this enzyme. Further study in human will allow a better comprehension about the use of epiT in drug abuse testing; it will also help to clarify the importance of its accumulation in breast cyst fluid and prostate, as well as its potential role as natural antiandrogen.
Figures

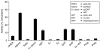
Similar articles
-
Assessment of steroidogenesis and steroidogenic enzyme functions.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;137:176-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.05.017. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23770321 Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding mouse 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: an androgen-inactivating enzyme selectively expressed in female tissues.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Jan;98(1):18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Sep 26. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16191478
-
Human type 3 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (aldo-keto reductase 1C2) and androgen metabolism in prostate cells.Endocrinology. 2003 Jul;144(7):2922-32. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0032. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12810547
-
Androgen inactivation and steroid-converting enzyme expression in abdominal adipose tissue in men.J Endocrinol. 2006 Dec;191(3):637-49. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06365. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 17170221
-
Pathways and genes involved in steroid hormone metabolism in male pigs: a review and update.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;140:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24239507 Review.
Cited by
-
Androgenic potential of human fetal adrenals at the end of the first trimester.Endocr Connect. 2017 Aug;6(6):348-359. doi: 10.1530/EC-17-0085. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Endocr Connect. 2017. PMID: 28592511 Free PMC article.
-
Intracrine Regulation of Estrogen and Other Sex Steroid Levels in Endometrium and Non-gynecological Tissues; Pathology, Physiology, and Drug Discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 19;9:940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00940. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30283331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracrine androgen biosynthesis, metabolism and action revisited.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 15;465:4-26. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.08.016. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28865807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An expanded metabolic pathway for androgen production by commensal bacteria.Nat Microbiol. 2025 May;10(5):1084-1098. doi: 10.1038/s41564-025-01979-9. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Nat Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40259019
-
Structure of 3(17)alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C21) holoenzyme from an orthorhombic crystal form: an insight into the bifunctionality of the enzyme.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Oct 1;63(Pt 10):825-30. doi: 10.1107/S1744309107040985. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007. PMID: 17909281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuoppasalmi K, Karjalainen U. Doping analysis in Helsinki 1983. In: Tehunen R, editor. Clinical Chemistry Research Foundation Publications. Helsinki, Painotalo Miktor; 1984. pp. 32–35.
-
- Clark LC, Kochakian CD. The in vitro metabolism of testosterone to 4-androstenedione-3,17 cis-testosterone and other steroids by rabbit liver slices. Journal of biological chemistry. 1947;170:22–23. - PubMed
-
- Arimasa N, Kochakian CD. Epitestosterone and 5alpha-androstane-3alpha,17beta-diol: the characteristic metabolites of androst-4-ene-3,17-dione produced by mouse kidney in vitro. Endocrinology. 1973;92:72–82. - PubMed
-
- Martin RP. Fecal metabolites of testosterone-4-14C in the bovine male castrate. Endocrinology. 1966;78:907–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

