Reversed-phase HPLC with UV detection for the determination of N-acetylaspartate and creatine
- PMID: 16018872
- PMCID: PMC1482469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.004
Reversed-phase HPLC with UV detection for the determination of N-acetylaspartate and creatine
Figures
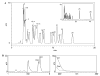
Similar articles
-
Anterior cingulate N-acetylaspartate/creatine ratios during clonidine treatment in a maltreated child with posttraumatic stress disorder.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001 Fall;11(3):311-6. doi: 10.1089/10445460152595649. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11642482
-
Ion-pairing high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the detection of N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylglutamate in cerebral tissue extracts.Anal Biochem. 2000 Jan 1;277(1):104-8. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4386. Anal Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10610694
-
Evaluation of contactless conductivity detection for the determination of UV absorbing and non-UV absorbing species in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2006 Feb 24;1107(1-2):159-64. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2005.12.060. Epub 2006 Jan 18. J Chromatogr A. 2006. PMID: 16412448
-
A new method for determination of buformin in plasma and urine by ion-paired reversed-phase HPLC with ultraviolet detection.Biomed Chromatogr. 2002 Oct;16(7):453-4. doi: 10.1002/bmc.182. Biomed Chromatogr. 2002. PMID: 12378556
-
Determination of apovincaminic acid in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography using solid-phase extraction and ultraviolet detection.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006 Jan 18;830(2):201-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.10.052. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16321580
Cited by
-
Deletion of the creatine transporter gene in neonatal, but not adult, mice leads to cognitive deficits.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019 Sep;42(5):966-974. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12137. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019. PMID: 31209903 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro studies on the putative function of N-acetylaspartate as an osmoregulator.Neurochem Res. 2007 Jul;32(7):1248-55. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9300-6. Epub 2007 Mar 31. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17401659
-
Stimulated efflux of amino acids and glutathione from cultured hippocampal slices by omission of extracellular calcium: likely involvement of connexin hemichannels.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 18;283(16):10347-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704153200. Epub 2008 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18272524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tranberg M, Stridh MH, Guy Y, Jilderos B, Wigstrom H, Weber SG, Sandberg M. NMDA-receptor mediated efflux of N-acetylaspartate: physiological and/or pathological importance? Neurochem Int. 2004;45:1195–1204. - PubMed
-
- Clark JB. N-acetyl aspartate: a marker for neuronal loss or mitochondrial dysfunction. Dev Neurosci. 1998;20:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Koller KJ, Zaczek R, Coyle JT. N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate: regional levels in rat brain and the effects of brain lesions as determined by a new HPLC method. J Neurochem. 1984;43:1136–1142. - PubMed
-
- Wollenberger A. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of creatinine. Acta Chem Scand. 1953;7:445–446.
-
- Dash AK, Sawhney A. A simple LC method with UV detection for the analysis of creatine and creatinine and its application to several creatine formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002;29:939–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

