TASK-like K+ channels mediate effects of 5-HT and extracellular pH in rat dorsal vagal neurones in vitro
- PMID: 16020457
- PMCID: PMC1474773
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.093070
TASK-like K+ channels mediate effects of 5-HT and extracellular pH in rat dorsal vagal neurones in vitro
Abstract
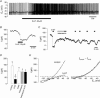
Dorsal vagal neurones (DVN) receive serotonergic projections from the medullary raphé nuclei, suggesting that 5-HT modulates vagal activity. A previous study has shown that 5-HT excites DVN in part by inhibition of a K+ current via postsynaptic 5-HT2A receptors. As mRNA for the two-pore-domain K+ channels TASK-1 (KCNK3) and TASK-3 (KCNK9) has been found in DVN, we investigated the possibility that 5-HT exerts its effects via inhibition of these K+ channels using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques. In current clamp, 5-HT (20 microM) elicited a depolarization by 5.1+/-1.5 mV and an increase in firing rate. In voltage clamp, 5-HT reduced the standing outward current (ISO) at -20 mV by 106+/-17 pA, inhibiting a conductance (reversal, -95+/-4 mV) which displayed Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz outward rectification, supportive of a TASK-like K+ current. Since TASK channels are modulated by extracellular pH (pHo), we next investigated the pH sensitivity of ISO in Hepes-buffered ACSF. At pHo 7.3, DVN exhibited an ISO of 147+/-15 pA at -20 mV. Acidification to pHo 6.3 reduced ISO to 85+/-13 pA, whereas raising pHo to 8.5 increased ISO to 216+/-26 pA. At pHo 7.3, ISO was inhibited by BaCl2 (IC50 465 microM), but unaffected by ZnCl2 (100 microM). 5-HT (10 microM) reduced ISO by 114+/-17 pA at pHo 7.3, but at pHo 6.3 the 5-HT-induced inhibition of ISO was significantly smaller. The present data suggest that the excitatory effects of 5-HT on DVN are mediated in part by inhibition of a TASK-like, pH-sensitive K+ conductance. The pharmacological profile of this conductance excludes TASK-3 homomers, but rather implicates TASK-1-containing channels.
Figures




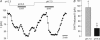
References
-
- Ballantyne D, Scheid P. Central chemosensitivity of respiration: a brief overview. Respir Physiol. 2001;129:5–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

