Cerebral hypoplasia and craniofacial defects in mice lacking heparan sulfate Ndst1 gene function
- PMID: 16020517
- PMCID: PMC7851831
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.01935
Cerebral hypoplasia and craniofacial defects in mice lacking heparan sulfate Ndst1 gene function
Abstract
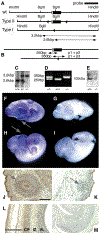
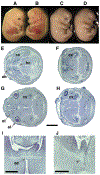
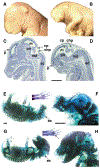
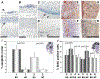
Mutant mice bearing a targeted disruption of the heparan sulfate (HS) modifying enzyme GlcNAc N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 (Ndst1) exhibit severe developmental defects of the forebrain and forebrain-derived structures, including cerebral hypoplasia, lack of olfactory bulbs, eye defects and axon guidance errors. Neural crest-derived facial structures are also severely affected. We show that properly synthesized heparan sulfate is required for the normal development of the brain and face, and that Ndst1 is a modifier of heparan sulfate-dependent growth factor/morphogen signalling in those tissues. Among the multiple heparan sulfate-binding factors potentially affected in Ndst1 mutant embryos, the facial phenotypes are consistent with impaired sonic hedgehog (Shh) and fibroblast growth factor (Fgf) interaction with mutant heparan sulfate. Most importantly, the data suggest the possibility that defects in heparan sulfate synthesis could give rise to or contribute to a number of developmental brain and facial defects in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Abzhanov A and Tabin CJ (2004). Shh and Fgf8 act synergistically to drive cartilage outgrowth during cranial development. Dev. Biol 273, 134–148. - PubMed
-
- Ahlgren SC and Bronner-Fraser M (1999). Inhibition of sonic hedgehog signaling in vivo results in craniofacial neural crest cell death. Curr. Biol 9, 1304–1314. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa J, Grobe K, Tsujimoto M and Esko JD (2001). Multiple Isozymes of Heparan Sulfate/Heparin GlcNAc N-Deacetylase/N-Sulfotransferase: Structure and Activity of the Fourth Member, NDST4. J. Biol. Chem 276, 5876–5882. - PubMed
-
- Bennett KL, Bradshaw J, Youngman T, Rodgers J, Greenfield B, Aruffo A and Linsley PS (1997). Deleted in colorectal carcinoma (DCC) binds heparin via its fifth fibronectin type III domain. J. Biol. Chem 272, 26940–26946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

