FRISC score for selection of patients for an early invasive treatment strategy in unstable coronary artery disease
- PMID: 16020594
- PMCID: PMC1769057
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.031369
FRISC score for selection of patients for an early invasive treatment strategy in unstable coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: To develop a scoring system for risk stratification and evaluation of the effect of an early invasive strategy for treatment of unstable coronary artery disease (CAD).
Design: Retrospective analysis of a randomised study (FRISC II; fast revascularisation in instability in coronary disease).
Setting: 58 Scandinavian hospitals.
Patients: 2457 patients with unstable CAD from the FRISC II study.
Main outcome measures: One year rates of mortality and death/myocardial infarction (MI).
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to an early invasive or a non-invasive strategy. From the non-invasive cohort independent variables of death or death/MI were identified.
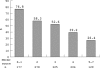
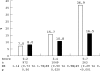
Results: Seven factors, age > 70 years, male sex, diabetes, previous MI, ST depression, and increased concentrations of troponins and markers of inflammation (interleukin 6 or C reactive protein), were associated with an independent increased risk for death or death/MI. In patients with > or = 5 of these factors the invasive strategy reduced mortality from 15.4% (20 of 130) to 5.2% (7 of 134) (risk ratio (RR) 0.34, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.15 to 0.78, p = 0.006). Death/MI was also reduced in patients with 3-4 factors from 15.7% (80 of 511) to 10.8% (58 of 538) (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.94, p = 0.02). Neither death nor death/MI was reduced in patients with 0-2 risk factors.
Conclusion: In unstable CAD, this scoring system based on factors independently associated with an adverse outcome can be used shortly after admission to the hospital for risk stratification and for selection of patients to an early invasive treatment strategy.
Figures



References
-
- FRISC II Investigators. Invasive compared with non-invasive treatment in unstable coronary- artery disease: FRISC II prospective randomised multicentre study. FRagmin and Fast Revascularisation during InStability in Coronary artery disease Investigators. Lancet 1999;354:708–15. - PubMed
-
- Wallentin L, Lagerqvist B, Husted S, et al. Outcome at 1 year after an invasive compared with a non-invasive strategy in unstable coronary-artery disease: the FRISC II invasive randomised trial. FRISC II Investigators. Fast revascularisation during instability in coronary artery disease. Lancet 2000;356:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Weintraub WS, Demopoulos LA, et al. Comparison of early invasive and conservative strategies in patients with unstable coronary syndromes treated with the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor tirofiban. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1879–87. - PubMed
-
- Fox KA, Poole-Wilson PA, Henderson RA, et al. Interventional versus conservative treatment for patients with unstable angina or non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: the British Heart Foundation RITA 3 randomised trial. Randomized intervention trial of unstable angina. Lancet 2002;360:743–51. - PubMed
-
- Savonitto S, Ardissino D, Granger CB, et al. Prognostic value of the admission electrocardiogram in acute coronary syndromes. JAMA 1999;281:707–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
