Evidence for ectopic neurotransmission at a neuronal synapse
- PMID: 16020730
- PMCID: PMC2915764
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1108239
Evidence for ectopic neurotransmission at a neuronal synapse
Abstract
Neurotransmitter release is well known to occur at specialized synaptic regions that include presynaptic active zones and postsynaptic densities. At cholinergic synapses in the chick ciliary ganglion, however, membrane formations and physiological measurements suggest that release distant from postsynaptic densities can activate the predominantly extrasynaptic alpha7 nicotinic receptor subtype. We explored such ectopic neurotransmission with a novel model synapse that combines Monte Carlo simulations with high-resolution serial electron microscopic tomography. Simulated synaptic activity is consistent with experimental recordings of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents only when ectopic transmission is included in the model, broadening the possibilities for mechanisms of neuronal communication.
Figures
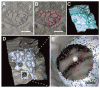
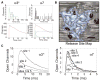
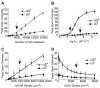
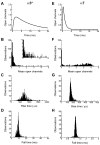

Comment in
-
Neuroscience. Monte Carlo places strong odds on ectopic release.Science. 2005 Jul 15;309(5733):387-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1115632. Science. 2005. PMID: 16020717 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DC03192/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068630/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS012601/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20-GM065805/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR04050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS12601/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR004050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P20 GM065805/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM068630/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-NS044306/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR006009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS35469/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR06009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS044306/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035469/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

