A review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in schizophrenia
- PMID: 16023676
- PMCID: PMC2768134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2005.05.005
A review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in schizophrenia
Abstract
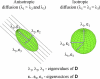
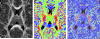
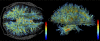
Both post-mortem and neuroimaging studies have contributed significantly to what we know about the brain and schizophrenia. MRI studies of volumetric reduction in several brain regions in schizophrenia have confirmed early speculations that the brain is disordered in schizophrenia. There is also a growing body of evidence suggesting that a disturbance in connectivity between different brain regions, rather than abnormalities within the separate regions themselves, are responsible for the clinical symptoms and cognitive dysfunctions observed in this disorder. Thus an interest in white matter fiber tracts, subserving anatomical connections between distant, as well as proximal, brain regions, is emerging. This interest coincides with the recent advent of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which makes it possible to evaluate the organization and coherence of white matter fiber tracts. This is an important advance as conventional MRI techniques are insensitive to fiber tract direction and organization, and have not consistently demonstrated white matter abnormalities. DTI may, therefore, provide important new information about neural circuitry, and it is increasingly being used in neuroimaging studies of psychopathological disorders. Of note, in the past five years 18 DTI studies in schizophrenia have been published, most describing white matter abnormalities. Questions still remain, however, regarding what we are measuring that is abnormal in this disease, and how measures obtained using one method correspond to those obtained using other methods? Below we review the basic principles involved in MR-DTI, followed by a review of the different methods used to evaluate diffusion. Finally, we review MR-DTI findings in schizophrenia.
Figures
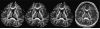


References
-
- Agartz I, Andersson JL, Skare S. Abnormal brain white matter in schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroreport. 2001;12(10):2251–4. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hetrick WP, Bunney WE, Jr, Jones EG. Maldistribution of interstitial neurons in prefrontal white matter of the brains of schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1996;53(5):425–36. - PubMed
-
- Ardekani BA, Nierenberg J, Hoptman MJ, Javitt DC, Lim KO. MRI study of white matter diffusion anisotropy in schizophrenia. Neuroreport. 2003;14(16):2025–9. - PubMed
-
- Bammer R, Auer M, Keeling SL, Augustin M, Stables LA, Prokesch RW, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging using single-shot SENSE-EPI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;48(1):128–36. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR in Biomedicine. 1995;8(7–8):333–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH040799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 50747/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 MH 01110/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013218/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 40799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR13218/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039335/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS 39335/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH068464-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH068464/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH077230/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 MH001110/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

