Docking kinetics and equilibrium of a GAAA tetraloop-receptor motif probed by single-molecule FRET
- PMID: 16024731
- PMCID: PMC1180751
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408645102
Docking kinetics and equilibrium of a GAAA tetraloop-receptor motif probed by single-molecule FRET
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13351
Abstract
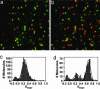
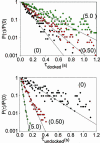
Docking kinetics and equilibrium of fluorescently labeled RNA molecules are studied with single-molecule FRET methods. Time-resolved FRET is used to monitor docking/undocking transitions for RNAs containing a single GAAA tetraloop-receptor tertiary interaction connected by a flexible single-stranded linker. The rate constants for docking and undocking are measured as a function of Mg2+, revealing a complex dependence on metal ion concentration. Despite the simplicity of this model system, conformational heterogeneity similar to that noted in more complex RNA systems is observed; relatively rapid docking/undocking transitions are detected for approximately two-thirds of the RNA molecules, with significant subpopulations exhibiting few or no transitions on the 10- to 30-s time scale for photobleaching. The rate constants are determined from analysis of probability densities, which allows a much wider range of time scales to be analyzed than standard histogram procedures. The data for the GAAA tetraloop receptor are compared with kinetic and equilibrium data for other RNA tertiary interactions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metal ion dependence, thermodynamics, and kinetics for intramolecular docking of a GAAA tetraloop and receptor connected by a flexible linker.Biochemistry. 2006 Mar 21;45(11):3664-73. doi: 10.1021/bi0520941. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16533049 Free PMC article.
-
The role of counterion valence and size in GAAA tetraloop-receptor docking/undocking kinetics.J Mol Biol. 2012 Oct 19;423(2):198-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.006. Epub 2012 Jul 14. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22796627
-
Site-directed spin labeling studies reveal solution conformational changes in a GAAA tetraloop receptor upon Mg(2+)-dependent docking of a GAAA tetraloop.J Mol Biol. 2005 Aug 5;351(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.06.007. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15993422
-
Probing the kinetic and thermodynamic consequences of the tetraloop/tetraloop receptor monovalent ion-binding site in P4-P6 RNA by smFRET.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Apr;43(2):172-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20140268. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 25849913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An RNA folding motif: GNRA tetraloop-receptor interactions.Q Rev Biophys. 2013 Aug;46(3):223-64. doi: 10.1017/S0033583513000048. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Q Rev Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23915736 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetic and thermodynamic framework for P4-P6 RNA reveals tertiary motif modularity and modulation of the folding preferred pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):E4956-65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525082113. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27493222 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule studies of group II intron ribozymes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 16;105(37):13853-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804034105. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18772388 Free PMC article.
-
Molecule by molecule, the physics and chemistry of life: SMB 2007.Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Apr;3(4):193-7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0407-193. Nat Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17372599 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent RNA motifs as scaffolds for genetically encodable small-molecule biosensors.Nat Chem Biol. 2017 Mar;13(3):295-301. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2278. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Nat Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28092358 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting ion-nucleic acid interactions by energy landscape-guided sampling.J Chem Theory Comput. 2012 Jun 12;8(6):2095-2101. doi: 10.1021/ct300227a. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012. PMID: 23002389 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

