The Bloom's syndrome helicase promotes the annealing of complementary single-stranded DNA
- PMID: 16024743
- PMCID: PMC1176015
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki712
The Bloom's syndrome helicase promotes the annealing of complementary single-stranded DNA
Abstract
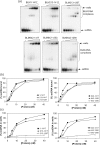
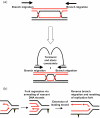
The product of the gene mutated in Bloom's syndrome, BLM, is a 3'-5' DNA helicase belonging to the highly conserved RecQ family. In addition to a conventional DNA strand separation activity, BLM catalyzes both the disruption of non-B-form DNA, such as G-quadruplexes, and the branch migration of Holliday junctions. Here, we have characterized a new activity for BLM: the promotion of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) annealing. This activity does not require Mg(2+), is inhibited by ssDNA binding proteins and ATP, and is dependent on DNA length. Through analysis of various truncation mutants of BLM, we show that the C-terminal domain is essential for strand annealing and identify a 60 amino acid stretch of this domain as being important for both ssDNA binding and strand annealing. We present a model in which the ssDNA annealing activity of BLM facilitates its role in the processing of DNA intermediates that arise during repair of damaged replication forks.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Bloom's syndrome gene product promotes branch migration of holliday junctions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 6;97(12):6504-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.100448097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10823897 Free PMC article.
-
BLM helicase facilitates Mus81 endonuclease activity in human cells.Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;65(7):2526-31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2421. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15805243
-
The mismatch DNA repair heterodimer, hMSH2/6, regulates BLM helicase.Oncogene. 2004 May 6;23(21):3749-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207462. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15064730
-
Role of the BLM helicase in replication fork management.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):936-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17363339 Review.
-
Roles of the Bloom's syndrome helicase in the maintenance of genome stability.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1456-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0331456. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246145 Review.
Cited by
-
Human RecQ Helicases in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 25;9:640755. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640755. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33718381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keeping ribosomal DNA intact: a repeating challenge.Chromosome Res. 2019 Mar;27(1-2):57-72. doi: 10.1007/s10577-018-9594-z. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Chromosome Res. 2019. PMID: 30556094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical analysis of human PIF1 helicase and functions of its N-terminal domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(19):6295-308. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn609. Epub 2008 Oct 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18835853 Free PMC article.
-
Replication fork regression in vitro by the Werner syndrome protein (WRN): holliday junction formation, the effect of leading arm structure and a potential role for WRN exonuclease activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(17):5729-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm561. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17717003 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the pathogenic SNPs in BLM helicase and their biological consequences by computational approach.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 23;10(1):12377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69033-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32704157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- German J. Bloom's syndrome. Dermatol. Clin. 1995;13:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Hickson I.D. RecQ helicases: caretakers of the genome. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Li J.L., Harrison R.J., Reszka A.P., Brosh R.M., Jr, Bohr V.A., Neidle S., Hickson I.D. Inhibition of the Bloom's and Werner's syndrome helicases by G-quadruplex interacting ligands. Biochemistry. 2001;40:15194–15202. - PubMed

