Bacillus subtilis RecU Holliday-junction resolvase modulates RecA activities
- PMID: 16024744
- PMCID: PMC1176016
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki713
Bacillus subtilis RecU Holliday-junction resolvase modulates RecA activities
Abstract
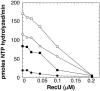
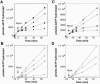
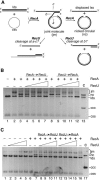
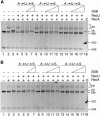
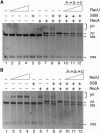
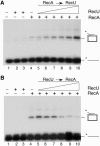
The Bacillus subtilis RecU protein is able to catalyze in vitro DNA strand annealing and Holliday-junction resolution. The interaction between the RecA and RecU proteins, in the presence or absence of a single-stranded binding (SSB) protein, was studied. Substoichiometric amounts of RecU enhanced RecA loading onto single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and stimulated RecA-catalyzed D-loop formation. However, RecU inhibited the RecA-mediated three-strand exchange reaction and ssDNA-dependent dATP or rATP hydrolysis. The addition of an SSB protein did not reverse the negative effect exerted by RecU on RecA function. Annealing of circular ssDNA and homologous linear 3'-tailed double-stranded DNA by RecU was not affected by the addition of RecA both in the presence and in the absence of SSB. We propose that RecU modulates RecA activities by promoting RecA-catalyzed strand invasion and inhibiting RecA-mediated branch migration, by preventing RecA filament disassembly, and suggest a potential mechanism for the control of resolvasome assembly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RecU Holliday junction resolvase acts at early stages of homologous recombination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(16):5242-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn500. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18684995 Free PMC article.
-
The stalk region of the RecU resolvase is essential for Holliday junction recognition and distortion.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jul 1;410(1):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 12. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21600217
-
Enhancement of Escherichia coli RecA protein enzymatic function by dATP.Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5871-81. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a025. Biochemistry. 1989. PMID: 2673351
-
The cell pole: the site of cross talk between the DNA uptake and genetic recombination machinery.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Nov-Dec;47(6):531-55. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2012.729562. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23046409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Homologous DNA transferase RecA: functional activities and the search for homology by recombining DNA molecules].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007 May-Jun;41(3):467-77. doi: 10.1134/s0026893307030132. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007. PMID: 17685224 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Bacillus subtilis RecA and its accessory factors, RecF, RecO, RecR and RecX, are required for spore resistance to DNA double-strand break.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(4):2295-307. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1194. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24285298 Free PMC article.
-
RecO-mediated DNA homology search and annealing is facilitated by SsbA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Nov;38(20):6920-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq533. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20581116 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis RecO nucleates RecA onto SsbA-coated single-stranded DNA.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24837-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802002200. Epub 2008 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18599486 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis DisA regulates RecA-mediated DNA strand exchange.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jun 4;47(10):5141-5154. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz219. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30916351 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic structures of Bacillus subtilis RecN-DNA complexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(1):110-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm759. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 17999999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kowalczykowski S.C. Initiation of genetic recombination and recombination-dependent replication. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000;25:156–165. - PubMed
-
- Chedin F., Kowalczykowski S.C. A novel family of regulated helicases/nucleases from Gram-positive bacteria: insights into the initiation of DNA recombination. Mol. Microbiol. 2002;43:823–834. - PubMed
-
- Morimatsu K., Kowalczykowski S.C. RecFOR proteins load RecA protein onto gapped DNA to accelerate DNA strand exchange: a universal step of recombinational repair. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:1337–1347. - PubMed
-
- Cox M.M., Goodman M.F., Kreuzer K.N., Sherratt D.J., Sandler S.J., Marians K.J. The importance of repairing stalled replication forks. Nature. 2000;404:37–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

