Binding of hnRNP L to the pre-mRNA processing enhancer of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene enhances both polyadenylation and nucleocytoplasmic export of intronless mRNAs
- PMID: 16024770
- PMCID: PMC1190326
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.15.6303-6313.2005
Binding of hnRNP L to the pre-mRNA processing enhancer of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene enhances both polyadenylation and nucleocytoplasmic export of intronless mRNAs
Abstract
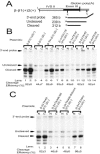
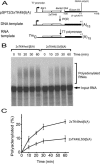
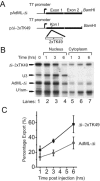
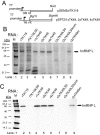
Liu and Mertz (Genes Dev. 9:1766-1780, 1995) previously identified a 119-nt pre-mRNA processing enhancer (PPE) element within the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene that enables intron-independent gene expression in higher eukaryotes by binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (hnRNP L). Here, we identify a 49-nt subelement within this PPE that enhanced stability, polyadenylation, and cytoplasmic accumulation of transcripts synthesized in CV-1 cells from an intronless variant of the human beta-globin gene when present in two or more tandem copies. This 2xTK49 PPE also enhanced (i) the efficiency of polyadenylation of intronless beta-globin RNA in a cell-free polyadenylation system and (ii) the kinetics of nucleocytoplasmic export of an intronless variant of adenovirus major late leader region RNA in Xenopus oocytes. This 2xTK49 PPE bound only hnRNP L. Analysis of 2xTK49 PPE mutants showed a strong positive correlation existed between binding hnRNP L and enhancement of intronless beta-globin gene expression. hnRNP L was found to associate with both the mRNA export factor TAP and the exon-exon junction complex protein Aly/REF. Thus, we conclude that hnRNP L plays roles in enhancing stability, polyadenylation, and nucleocytoplasmic export; it does so, at least in part, by directly recruiting to intronless PPE-containing RNAs cofactors normally recruited to intron-containing RNAs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pre-mRNA processing enhancer (PPE) elements from intronless genes play additional roles in mRNA biogenesis than do ones from intron-containing genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 20;33(7):2215-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki506. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15843684 Free PMC article.
-
HnRNP L binds a cis-acting RNA sequence element that enables intron-dependent gene expression.Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 15;9(14):1766-80. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.14.1766. Genes Dev. 1995. PMID: 7542615
-
Intronless mRNA transport elements may affect multiple steps of pre-mRNA processing.EMBO J. 1999 Mar 15;18(6):1642-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.6.1642. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10075934 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus regulatory protein UL69 and its effect on mRNA export.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2939-49. doi: 10.2741/2899. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981767 Review.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) in cellular processes: Focus on hnRNP E1's multifunctional regulatory roles.RNA. 2010 Aug;16(8):1449-62. doi: 10.1261/rna.2254110. Epub 2010 Jun 28. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20584894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase sequence fused to the lacz gene increases levels of {beta}-galactosidase activity per genome of high-capacity but not first-generation adenoviral vectors in vitro and in vivo.J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(4):2004-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01298-08. Epub 2008 Dec 10. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19073729 Free PMC article.
-
Auto- and cross-regulation of the hnRNP L proteins by alternative splicing.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;29(6):1442-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01689-08. Epub 2009 Jan 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19124611 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and Cellular Components of AAV2 Replication Compartments.Open Virol J. 2013 Oct 31;7:98-120. doi: 10.2174/1874357901307010098. eCollection 2013. Open Virol J. 2013. PMID: 24222808 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPL expression dynamics in the embryo and placenta.Gene Expr Patterns. 2023 Jun;48:119319. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2023.119319. Epub 2023 May 4. Gene Expr Patterns. 2023. PMID: 37148985 Free PMC article.
-
The heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L is an essential component in the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV-regulated alternative splicing through cytidine-adenosine repeats.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 16;284(3):1505-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805113200. Epub 2008 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19017650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1987. Preparation of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts from mammalian cells, p. 12.1.1-12.1.9. In V. B. Chanda (ed.), Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
