Components of the ESCRT pathway, DFG16, and YGR122w are required for Rim101 to act as a corepressor with Nrg1 at the negative regulatory element of the DIT1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 16024810
- PMCID: PMC1190364
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.15.6772-6788.2005
Components of the ESCRT pathway, DFG16, and YGR122w are required for Rim101 to act as a corepressor with Nrg1 at the negative regulatory element of the DIT1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
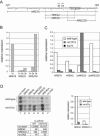
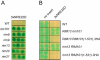
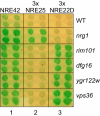
The divergently transcribed DIT1 and DIT2 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which belong to the mid-late class of sporulation-specific genes, are subject to Ssn6-Tup1-mediated repression in mitotic cells. The Ssn6-Tup1 complex, which is required for repression of diverse sets of coordinately regulated genes, is known to be recruited to target genes by promoter-specific DNA-binding proteins. In this study, we show that a 42-bp negative regulatory element (NRE) present in the DIT1-DIT2 intergenic region consists of two distinct subsites and that a multimer of each subsite supports efficient Ssn6-Tup1-dependent repression of a CYC1-lacZ reporter gene. By genetic screening procedures, we identified DFG16, YGR122w, VPS36, and the DNA-binding proteins Rim101 and Nrg1 as potential mediators of NRE-directed repression. We show that Nrg1 and Rim101 bind simultaneously to adjacent target sites within the NRE in vitro and act as corepressors in vivo. We have found that the ability of Rim101 to be proteolytically processed to its active form and mediate NRE-directed repression not only depends on the previously characterized RIM signaling pathway but also requires Dfg16, Ygr122w, and components of the ESCRT trafficking pathway. Interestingly, Rim101 was processed in bro1 and doa4 strains but was unable to mediate efficient repression.
Figures

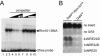


Similar articles
-
An Ssn6-Tup1-dependent negative regulatory element controls sporulation-specific expression of DIT1 and DIT2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jan;17(1):123-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.1.123. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 8972192 Free PMC article.
-
Sporulation-specific expression of the yeast DIT1/DIT2 promoter is controlled by a newly identified repressor element and the short form of Rim101p.Eur J Biochem. 1998 Dec 1;258(2):430-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2580430.x. Eur J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9874208
-
Spe3, which encodes spermidine synthase, is required for full repression through NRE(DIT) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 1998 Sep;150(1):59-73. doi: 10.1093/genetics/150.1.59. Genetics. 1998. PMID: 9725830 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional repression by Tup1-Ssn6.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):437-43. doi: 10.1139/o06-073. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936817 Review.
-
Rox1 mediated repression. Oxygen dependent repression in yeast.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;475:185-95. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10849660 Review.
Cited by
-
Inferring transcriptional modules from ChIP-chip, motif and microarray data.Genome Biol. 2006;7(5):R37. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-5-r37. Epub 2006 May 5. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16677396 Free PMC article.
-
Sporulation in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2011 Nov;189(3):737-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.127126. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 22084423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the exomer complex in the polarized transport of Ena1 required for Saccharomyces cerevisiae survival against toxic cations.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Dec 1;28(25):3672-3685. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-09-0549. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 29021337 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of Aspergillus nidulans severely debilitating null mutations in ESCRT-0, I, II and III genes by inactivation of a salt-tolerance pathway allows examination of ESCRT gene roles in pH signalling.J Cell Sci. 2011 Dec 1;124(Pt 23):4064-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.088344. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 22135362 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor Nrg1 mediates capsule formation, stress response, and pathogenesis in Cryptococcus neoformans.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Jul;5(7):1147-56. doi: 10.1128/EC.00145-06. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16835458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arst, H. N., and M. A. Penalva. 2003. pH regulation in Aspergillus and parallels with higher eukaryotic regulatory systems. Trends Genet. 19:224-231. - PubMed
-
- Babst, M., D. J. Katzmann, E. J. Estepa-Sabal, T. Meerloo, and S. D. Emr. 2002. ESCRT-III: an endosome-associated heterooligomeric protein complex required for MVB sorting. Dev. Cell 3:271-282. - PubMed
-
- Babst, M., D. J. Katzmann, W. B. Snyder, B. Wendland, and S. D. Emr. 2002. Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell 3:283-289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
