Cytokines and neutrophils as important mediators of platelet-activating factor-induced kinin B1 receptor expression
- PMID: 16025141
- PMCID: PMC1576273
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706327
Cytokines and neutrophils as important mediators of platelet-activating factor-induced kinin B1 receptor expression
Abstract
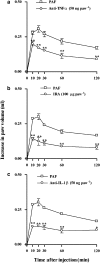
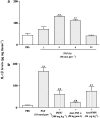
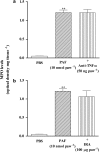
PAF injection into the rat paw is accompanied by the concomitant activation of NF-kappaB and neutrophil influx, which appears to be relevant to the up-regulation of kinin B1 receptors. Herein, we analyse the role of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta production for PAF-induced B1 receptor upregulation in the rat paw. Additionally, we evaluate how cytokine production and neutrophil migration fit into the temporal sequence of events leading to PAF-induced B1 receptor upregulation. In our experiments, treatment with PAF resulted in a marked increase of B1 receptor-mediated paw oedema and in situ production of TNF-alpha at 1 h and IL-1beta at 3 and 6 h later. B1 receptor-mediated paw oedema was significantly inhibited by anti-TNF-alpha antibody and by interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IRA). TNF-alpha was necessary for the local PAF-induced IL-1beta production. NF-kappaB blocker PDTC prevented the production of both TNF-alpha and IL-1beta, indicating that cytokine production is NF-kappaB dependent. Depletion of neutrophils with an anti-PMN antibody prevented IL-1beta, but not TNF-alpha, production. Although both TNF-alpha and IL-1beta are relevant to functional B1 receptor upregulation, PAF-induced increase in B1 receptor mRNA was markedly suppressed by anti-TNF-alpha and, to a lesser extent, by IRA. B1 receptor mRNA expression was also prevented by the anti-PMN antibody. In conclusion, the activation of the TNF-alpha/neutrophil axis by PAF seems to be sufficient for B1 receptor mRNA production. However, the TNF-alpha/neutrophil axis is also necessary for IL-1beta production. These two processes might lead to the appearance of functional kinin B1 upregulation receptors in vivo after PAF treatment.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanisms underlying the modulatory action of platelet activating factor (PAF) on the upregulation of kinin B1 receptors in the rat paw.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul;139(5):973-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705314. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12839871 Free PMC article.
-
Kinin B1 receptor up-regulation after lipopolysaccharide administration: role of proinflammatory cytokines and neutrophil influx.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1839-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1839. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734768
-
The role of migrating leukocytes in IL-1 beta-induced up-regulation of kinin B(1) receptors in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;135(5):1107-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704488. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11877316 Free PMC article.
-
PAF, cytokines, toxic oxygen products and cell injury.Mol Aspects Med. 1991;12(2):169-74. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(91)90012-b. Mol Aspects Med. 1991. PMID: 2072825 Review. No abstract available.
-
Cytokines and perinatal brain injury.Neurochem Int. 1997 Apr-May;30(4-5):375-83. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(96)00072-1. Neurochem Int. 1997. PMID: 9106251 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel Danshensu/tetramethylpyrazine protects against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in rats.Int J Med Sci. 2021 May 13;18(12):2716-2724. doi: 10.7150/ijms.59411. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34104104 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of the Calcium Channel Blocker CTK 01512-2 in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;55(12):9307-9327. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1049-1. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29667130
-
Kinin B1 receptors contributes to acute pain following minor surgery in humans.Mol Pain. 2010 Feb 13;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-12. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20152050 Free PMC article.
-
The role of P2X7 purinergic receptors in inflammatory and nociceptive changes accompanying cyclophosphamide-induced haemorrhagic cystitis in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;165(1):183-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01535.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21675966 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 Contributes to Cerebral Malaria Severity and Mortality by Regulating Brain Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 May 16;2019:9451671. doi: 10.1155/2019/9451671. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31223430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BARNES P.J., KARIN M. Nuclear factor-κB – a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- BHOOLA K.D., FIGUEROA C.D., WORTHY K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992;44:1–80. - PubMed
-
- BÖCKMANN S., PAEGELOW I. Kinins and kinin receptors: importance for the activation of leukocytes. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2000;68:587–592. - PubMed
-
- CALIXTO J.B., CABRINI D.A., FERREIRA J., CAMPOS M.M. Kinins in pain and inflammation. Pain. 2000;87:1–5. - PubMed
-
- CALIXTO J.B., CABRINI D.A., FERREIRA J., CAMPOS M.M. Inflammatory pain: kinins and antagonists. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2001;14:519–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

