The role of nuclear factor kappaB in late-gestation liver development in the rat
- PMID: 16025516
- PMCID: PMC8014986
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.20796
The role of nuclear factor kappaB in late-gestation liver development in the rat
Abstract
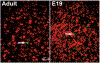
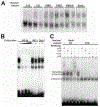
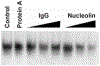
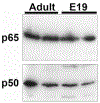
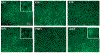
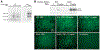
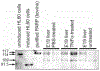
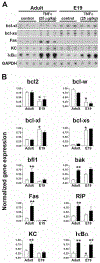
During the last 3 days of fetal development in the rodent, a burst of hepatocyte proliferation results in a tripling of liver size. Despite stimulation of mitogenesis via multiple signaling pathways, including some that are considered stress response pathways, little apoptosis accompanies this cell growth. Given the accepted role of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) in preventing hepatocellular apoptosis during proliferation in mid-development, we predicted that NF-kappaB would be functional during the period of rapid growth during late gestation in the rat. NF-kappaB binding in electrophoretic mobility shift assays was low in embryonic day (E) 19 liver nuclear extracts relative to adult liver nuclear extracts. An additional band that was present in E19 liver was purified and identified as nucleolin. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) administration to E19 embryos in utero produced minimal induction of NF-kappaB p50 homodimers and p50/p65 heterodimers, yet baseline apoptosis was not affected. Although p65 was present in E19 hepatocyte cytoplasm in amounts comparable to adult liver, we observed little translocation of p65 to the liver nuclei following TNF-alpha administration. Additionally, expression of several NF-kappaB-responsive genes remained minimally induced in E19 liver following TNF-alpha treatment. In conclusion, although the NF-kappaB components are present in late-gestation fetal liver, NF-kappaB as a transcription factor is relatively inactive and unresponsive to TNF-alpha. Given this finding and the high level of proliferation in late-gestation fetal liver, we predict that alternative antiapoptotic mechanisms are active during this period of rapid hepatic growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures
Comment in
-
Does nucleolin bind the NF kappa B DNA binding motif?Hepatology. 2006 Feb;43(2):376; author reply 376-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.21027. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16440351 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genetic inactivation of RelA/p65 sensitizes adult mouse hepatocytes to TNF-induced apoptosis in vivo and in vitro.Gastroenterology. 2007 Jun;132(7):2489-503. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.033. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17570221
-
Suppression of constitutive and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation and induction of apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells: correlation with down-regulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 May 1;10(9):3169-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0586. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15131058
-
Regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by the nuclear factor-kappaB heterodimers p65/p65 and p65/c-Rel in the absence of p50.Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Mar;8(3):335-42. Cell Growth Differ. 1997. PMID: 9056676
-
Persistent activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells involves the induction of potentially novel Rel-like factors and prolonged changes in the expression of IkappaB family proteins.Hepatology. 1999 Sep;30(3):761-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300327. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10462383
-
Hepatic tumor necrosis factor signaling and nuclear factor-kappaB: effects on liver homeostasis and beyond.Endocr Rev. 2007 Jun;28(4):365-86. doi: 10.1210/er.2006-0031. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Endocr Rev. 2007. PMID: 17431229 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolin regulates c-Jun/Sp1-dependent transcriptional activation of cPLA2alpha in phorbol ester-treated non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(1):217-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm1027. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18025046 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic translation control in the late-gestation fetal rat.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):R558-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00091.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18565838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 2004;18: 2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Delhase M. The I kappa B kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin Immunol 2000;12:85–98. - PubMed
-
- Leung TH, Hoffmann A, Baltimore D. One nucleotide in a kappaB site can determine cofactor specificity for NF-kappaB dimers. Cell 2004;118:453–464. - PubMed
-
- Chen LF, Greene WC. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004;5:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Ghosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
