Cancer cell adaptation to chemotherapy
- PMID: 16026610
- PMCID: PMC1199589
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-78
Cancer cell adaptation to chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Tumor resistance to chemotherapy may be present at the beginning of treatment, develop during treatment, or become apparent on re-treatment of the patient. The mechanisms involved are usually inferred from experiments with cell lines, as studies in tumor-derived cells are difficult. Studies of human tumors show that cells adapt to chemotherapy, but it has been largely assumed that clonal selection leads to the resistance of recurrent tumors.
Methods: Cells derived from 47 tumors of breast, ovarian, esophageal, and colorectal origin and 16 paired esophageal biopsies were exposed to anticancer agents (cisplatin; 5-fluorouracil; epirubicin; doxorubicin; paclitaxel; irinotecan and topotecan) in short-term cell culture (6 days). Real-time quantitative PCR was used to measure up- or down-regulation of 16 different resistance/target genes, and when tissue was available, immunohistochemistry was used to assess the protein levels.
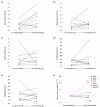
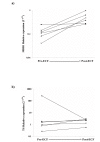
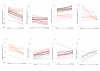
Results: In 8/16 paired esophageal biopsies, there was an increase in the expression of multi-drug resistance gene 1 (MDR1) following epirubicin + cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil (ECF) chemotherapy and this was accompanied by increased expression of the MDR-1 encoded protein, P-gp. Following exposure to doxorubicin in vitro, 13/14 breast carcinomas and 9/12 ovarian carcinomas showed >2-fold down-regulation of topoisomerase IIalpha (TOPOIIalpha). Exposure to topotecan in vitro, resulted in >4-fold down-regulation of TOPOIIalpha in 6/7 colorectal tumors and 8/10 ovarian tumors.
Conclusion: This study suggests that up-regulation of resistance genes or down-regulation in target genes may occur rapidly in human solid tumors, within days of the start of treatment, and that similar changes are present in pre- and post-chemotherapy biopsy material. The molecular processes used by each tumor appear to be linked to the drug used, but there is also heterogeneity between individual tumors, even those with the same histological type, in the pattern and magnitude of response to the same drugs. Adaptation to chemotherapy may explain why prediction of resistance mechanisms is difficult on the basis of tumor type alone or individual markers, and suggests that more complex predictive methods are required to improve the response rates to chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reversal effects of nomegestrol acetate on multidrug resistance in adriamycin-resistant MCF7 breast cancer cell line.Breast Cancer Res. 2001;3(4):253-63. doi: 10.1186/bcr303. Epub 2001 Apr 2. Breast Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11434876 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of GAS1 as an epirubicin resistance-related gene in human gastric cancer cells with a partially randomized small interfering RNA library.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 25;284(39):26273-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.028068. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19638344 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of an ATP-binding cassette superfamily transporter, multidrug resistance protein 2, in human colorectal carcinomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jun;6(6):2401-7. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10873092
-
Modulation and prevention of multidrug resistance by inhibitors of P-glycoprotein.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40 Suppl:S13-9. doi: 10.1007/s002800051055. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9272128 Review.
-
Irinotecan.2018 Apr 27. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2018 Apr 27. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643368 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic Activities of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Parent and Tamoxifen-Resistant T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells and Their Combination Effects with Tamoxifen against Resistant Cells.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010 Oct;2(4):187-96. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 23408729 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 Aug;10(8):472-84. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.110. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23836314 Review.
-
Schedule-dependent cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan in a colon cancer cell line.J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec;41(12):1149-57. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1904-0. Epub 2007 Feb 6. J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17287894
-
Resistance to anti-tubulin agents: From vinca alkaloids to epothilones.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Mar 19;2(1):82-106. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.06. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Extraordinary Response and Long-Term Remission of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) After [¹⁷⁷Lu]Lu-PSMA Radioligand Therapy Due to an Immunomodulatory Effect (Radiovaccination)? A Dual Center Experience on Super-Responders.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 31;17(3):476. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030476. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreotti PE, Linder D, Hartmann DM, Cree IA, Pazzagli M, Bruckner HW. TCA-100 tumour chemosensitivity assay: differences in sensitivity between cultured tumour cell lines and clinical studies. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1994;9:373–378. - PubMed
-
- Cree IA, Kurbacher CM, Untch M, Sutherland LA, Hunter EM, Subedi AM, James EA, Dewar JA, Preece PE, Andreotti PE. Correlation of the clinical response to chemotherapy in breast cancer with ex vivo chemosensitivity. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 1996;7:630–635. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto Y, Takano H, Fojo T. Cellular adaptation to drug exposure: evolution of the drug-resistant phenotype. Cancer Res . 1997;57:5086–5092. - PubMed
-
- Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Abolhoda A, Wilson AE, Ross H, Danenberg PV, Burt M, Scotto KW. Rapid activation of MDR1 gene expression in human metastatic sarcoma after in vivo exposure to doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:3352–3356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

