Identification and characterization of the mouse nuclear export factor (Nxf) family members
- PMID: 16027110
- PMCID: PMC1175460
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki706
Identification and characterization of the mouse nuclear export factor (Nxf) family members
Abstract
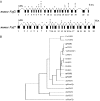
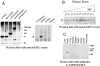
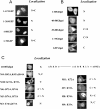
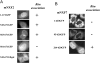
TAP/hNXF1 is a key factor that mediates general cellular mRNA export from the nucleus, and its orthologs are structurally and functionally conserved from yeast to humans. Metazoans encode additional proteins that share homology and domain organization with TAP/hNXF1, suggesting their participation in mRNA metabolism; however, the precise role(s) of these proteins is not well understood. Here, we found that the human mRNA export factor hNXF2 is specifically expressed in the brain, suggesting a brain-specific role in mRNA metabolism. To address the roles of additional NXF factors, we have identified and characterized the two Nxf genes, Nxf2 and Nxf7, which together with the TAP/hNXF1's ortholog Nxf1 comprise the murine Nxf family. Both mNXF2 and mNXF7 have a domain structure typical of the NXF family. We found that mNXF2 protein is expressed during mouse brain development. Similar to TAP/hNXF1, the mNXF2 protein is found in the nucleus, the nuclear envelope and cytoplasm, and is an active mRNA export receptor. In contrast, mNXF7 localizes exclusively to cytoplasmic granules and, despite its overall conserved sequence, lacks mRNA export activity. We concluded that mNXF2 is an active mRNA export receptor similar to the prototype TAP/hNXF1, whereas mNXF7 may have a more specialized role in the cytoplasm.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning and functional characterization of mouse Nxf family gene products.Genomics. 2005 May;85(5):641-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.01.003. Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15820316
-
Nuclear export factor family protein participates in cytoplasmic mRNA trafficking.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31981-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502736200. Epub 2005 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16014633
-
NXF1/p15 heterodimers are essential for mRNA nuclear export in Drosophila.RNA. 2001 Dec;7(12):1768-80. RNA. 2001. PMID: 11780633 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of nuclear export and cytoplasmic localization of mRNAs by NXF family proteins].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009 Dec;54(16 Suppl):2109-13. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009. PMID: 21089626 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
The Varicella-Zoster virus IE4 protein: a conserved member of the herpesviral mRNA export factors family and a potential alternative target in antiherpetic therapies.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):1973-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.07.011. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20650265 Review.
Cited by
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein FMRP binds mRNAs in the nucleus.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;29(1):214-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01377-08. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18936162 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear transport proteins: structure, function, and disease relevance.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 10;8(1):425. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01649-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37945593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of Nxf2 causes defects in male meiosis and age-dependent depletion of spermatogonia.Dev Biol. 2009 Jun 1;330(1):167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.03.022. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19345203 Free PMC article.
-
The fragile X mental retardation protein interacts with a distinct mRNA nuclear export factor NXF2.RNA. 2006 Aug;12(8):1446-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.94306. Epub 2006 Jun 21. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16790844 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of an Nxf7 knockout mouse to study NXF5 deficiency in a patient with intellectual disability.PLoS One. 2013 May 13;8(5):e64144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064144. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23675524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grüter P., Tabernero C., von Kobbe C., Schmitt C., Saavedra C., Bachi A., Wilm M., Felber B.K., Izaurralde E. TAP, the human homolog of Mex67p, mediates CTE-dependent RNA export from the nucleus. Mol. Cell. 1998;1:649–659. - PubMed
-
- Erkmann J.A., Kutay U. Nuclear export of mRNA: from the site of transcription to the cytoplasm. Exp. Cell Res. 2004;296:12–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

