Expansion and long-range differentiation of the NKT cell lineage in mice expressing CD1d exclusively on cortical thymocytes
- PMID: 16027237
- PMCID: PMC2213013
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20050413
Expansion and long-range differentiation of the NKT cell lineage in mice expressing CD1d exclusively on cortical thymocytes
Abstract
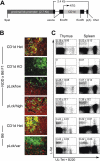
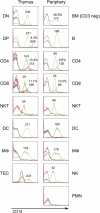
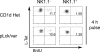
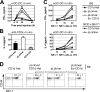
Unlike conventional major histocompatibility complex-restricted T cells, Valpha14-Jalpha18 NKT cell lineage precursors engage in cognate interactions with CD 1 d-expressing bone marrow-derived cells that are both necessary and sufficient for their thymic selection and differentiation, but the nature and sequence of these interactions remain partially understood. After positive selection mediated by CD1d-expressing cortical thymocytes, the mature NKT cell lineage undergoes a series of changes suggesting antigen priming by a professional antigen-presenting cell, including extensive cell division, acquisition of a memory phenotype, the ability to produce interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma, and the expression of a panoply of NK receptors. By using a combined transgenic and chimeric approach to restrict CD1d expression to cortical thymocytes and to prevent expression on other hematopoietic cell types such as dendritic cells, macrophages, or B cells, we found that, to a large extent, expansion and differentiation events could be imparted by a single-cognate interaction with CD1d-expressing cortical thymocytes. These surprising findings suggest that, unlike thymic epithelial cells, cortical thymocytes can provide unexpected, cell type-specific signals leading to lineage expansion and NKT cell differentiation.
Figures



References
-
- Godfrey, D.I., K.J. Hammond, L.D. Poulton, M.J. Smyth, and A.G. Baxter. 2000. NKT cells: facts, functions and fallacies. Immunol. Today. 21:573–583. - PubMed
-
- Brigl, M., and M.B. Brenner. 2004. CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:817–890. - PubMed
-
- Park, S.H., and A. Bendelac. 2000. CD1-restricted T-cell responses and microbial infection. Nature. 406:788–792. - PubMed
-
- Benlagha, K., T. Kyin, A. Beavis, L. Teyton, and A. Bendelac. 2002. A thymic precursor to the NKT cell lineage. Science. 296:553–555. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

