Application of serum SELDI proteomic patterns in diagnosis of lung cancer
- PMID: 16029516
- PMCID: PMC1183195
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-83
Application of serum SELDI proteomic patterns in diagnosis of lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Currently, no satisfactory biomarkers are available to screen for lung cancer. Surface-Enhanced Laser Desorption/ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry ProteinChip system (SELDI-TOF-MS) is one of the currently used techniques to identify biomarkers for cancers. The aim of this study is to explore the application of serum SELDI proteomic patterns to distinguish lung cancer patients from healthy individuals.
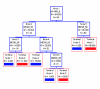
Methods: A total of 208 serum samples, including 158 lung cancer patients and 50 healthy individuals, were randomly divided into a training set (including 11 sera from patients with stages I/II lung cancer, 63 from patients with stages III/IV lung cancer and 20 from healthy controls) and a blinded test set (including 43 sera from patients with stages I/II lung cancer, 41 from patients with stages III/IV lung cancer and 30 from healthy controls). All samples were analyzed by SELDI technology. The spectra were generated on weak cation exchange (WCX2) chips, and protein peaks clustering and classification analyses were made using Ciphergen Biomarker Wizard and Biomarker Pattern software, respectively. We additionally determined Cyfra21-1 and NSE in the 208 serum samples included in this study using an electrochemiluminescent immunoassay.
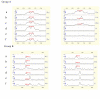
Results: Five protein peaks at 11493, 6429, 8245, 5335 and 2538 Da were automatically chosen as a biomarker pattern in the training set. When the SELDI marker pattern was tested with the blinded test set, it yielded a sensitivity of 86.9%, a specificity of 80.0% and a positive predictive value of 92.4%. The sensitivities provided by Cyfra21-1 and NSE used individually or in combination were significantly lower than that of the SELDI marker pattern (P < 0.005 or 0.05, respectively). Based on the results of the test set, we found that the SELDI marker pattern showed a sensitivity of 91.4% in the detection of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), which was significantly higher than that in the detection of small cell lung cancers (P < 0.05); The pattern also had a sensitivity of 79.1% in the detection of lung cancers in stages I/II.
Conclusion: These results suggest that serum SELDI protein profiling can distinguish lung cancer patients, especially NSCLC patients, from normal subjects with relatively high sensitivity and specificity, and the SELDI-TOF-MS is a potential tool for the screening of lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of lung cancer patients by serum protein profiling using surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Am J Clin Oncol. 2008 Apr;31(2):133-9. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e318145b98b. Am J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18391596
-
Five serum proteins identified using SELDI-TOF-MS as potential biomarkers of gastric cancer.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010 Apr;40(4):336-42. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyp175. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20089528
-
A serum proteomic pattern for the detection of colorectal adenocarcinoma using surface enhanced laser desorption and ionization mass spectrometry.Cancer Invest. 2006 Dec;24(8):747-53. doi: 10.1080/07357900601063873. Cancer Invest. 2006. PMID: 17162557
-
[Proteomic profiling: the potential of Seldi-Tof for the identification of new cancer biomarkers].Bull Cancer. 2005 Sep;92(9):763-8. Bull Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16203265 Review. French.
-
SELDI-TOF serum proteomics and colorectal cancer: a current overview.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2010 Oct-Dec;116(4-5):188-96. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2010.495130. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20615064 Review.
Cited by
-
Human body fluid proteome analysis.Proteomics. 2006 Dec;6(23):6326-53. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200600284. Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 17083142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of surfaces for liquid crystal-based bioanalytical assays.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010 Mar;2(3):722-31. doi: 10.1021/am900753v. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010. PMID: 20356273 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of SELDI Spectra Across Time and Laboratories.Cancer Inform. 2011 Mar 14;10:45-64. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S6438. Cancer Inform. 2011. PMID: 21552492 Free PMC article.
-
Serum biomarkers identification by mass spectrometry in high-mortality tumors.Int J Proteomics. 2013;2013:125858. doi: 10.1155/2013/125858. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Int J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23401773 Free PMC article.
-
Use of anchorchip-time-of-flight spectrometry technology to screen tumor biomarker proteins in serum for small cell lung cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2010 Sep 20;5:60. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-60. Diagn Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20854674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stieber P, Aronsson AC, Bialk P. Tumor markers in lung cancer: EGTM recommendations. Anticancer Res. 1999;19:2817–2819. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Jett JR, Hartman TE, Midthun DE, Sloan JA, Sykes AM, Aughenbaugh GL, Clemens MA. Lung cancer screening with CT: Mayo clinic experience. Radiology. 2003;226:756–761. - PubMed
-
- Kulpa J, Wojcik E, Reinfuss M, Kolodziejski L. Carcinoembryonic antigen, squamous cell carcinoma antigen, CYFRA21-1, and neuro-specific enolase in squamous cell lung cancer patients. Clin Chem. 2002;48:1931–1937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

