Functional characterization of a Na(+)-coupled dicarboxylate carrier protein from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 16030212
- PMCID: PMC1196027
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.15.5189-5194.2005
Functional characterization of a Na(+)-coupled dicarboxylate carrier protein from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
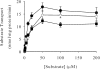
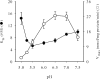
We have cloned and functionally characterized a Na(+)-coupled dicarboxylate transporter, SdcS, from Staphylococcus aureus. This carrier protein is a member of the divalent anion/Na(+) symporter (DASS) family and shares significant sequence homology with the mammalian Na(+)/dicarboxylate cotransporters NaDC-1 and NaDC-3. Analysis of SdcS function indicates transport properties consistent with those of its eukaryotic counterparts. Thus, SdcS facilitates the transport of the dicarboxylates fumarate, malate, and succinate across the cytoplasmic membrane in a Na(+)-dependent manner. Furthermore, kinetic work predicts an ordered reaction sequence with Na(+) (K(0.5) of 2.7 mM) binding before dicarboxylate (K(m) of 4.5 microM). Because this transporter and its mammalian homologs are functionally similar, we suggest that SdcS may serve as a useful model for DASS family structural analysis.
Figures

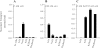


References
-
- Abramson, J., I. Smirnova, V. Kasho, G. Verner, H. R. Kaback, and S. Iwata. 2003. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 301:610-615. - PubMed
-
- Bai, L., and A. M. Pajor. 1997. Expression cloning of NaDC-2, an intestinal Na+- or Li+-dependent dicarboxylate transporter. Am. J. Physiol. 273:G267-G274. - PubMed
-
- Chang, G., and C. B. Roth. 2001. Structure of MsbA from E. coli: a homolog of the multidrug resistance ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters. Science 293:1793-1800. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. C., and T. H. Wilson. 1986. Solubilization and functional reconstitution of the proline transport system of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 261:2599-2604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

