NanA, a neuraminidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae, shows high levels of sequence diversity, at least in part through recombination with Streptococcus oralis
- PMID: 16030232
- PMCID: PMC1196044
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.15.5376-5386.2005
NanA, a neuraminidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae, shows high levels of sequence diversity, at least in part through recombination with Streptococcus oralis
Abstract
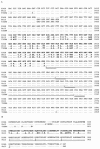
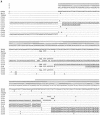
Streptococcus pneumoniae, an important human pathogen, contains at least two genes, nanA and nanB, that express sialidase activity. NanA is a virulence determinant of pneumococci which is important in animal models of colonization and middle ear infections. The gene encoding NanA was detected in all 106 pneumococcal strains screened that represented 59 restriction profiles. Sequencing confirmed a high level of diversity, up to 17.2% at the nucleotide level and 14.8% at the amino acid level. NanA diversity is due to a number of mechanisms including insertions, point mutations, and recombination generating mosaic genes. The level of nucleotide divergence for each recombinant block is greater than 30% and much higher than the 20% identified within mosaic pbp genes, suggesting that a high selective pressure exists for these alterations. These data indicate that at least one of the four recombinant blocks identified originated from a Streptococcus oralis isolate, demonstrating for the first time that protein virulence determinants of pneumococci have, as identified previously for genes encoding penicillin binding proteins, evolved by recombination with oral streptococci. No amino acid alterations were identified within the aspartic boxes or predicted active site, suggesting that sequence variation may be important in evading the adaptive immune response. Furthermore, this suggests that nanA is an important target of the immune system in the interaction between the pneumococcus and host.
Figures




References
-
- Beighton, D., and S. Alum. 1997. Use of repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR (REP-PCR) to study Streptococcus oralis. J. Dent. Res. 76:1026.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

