Myosin 2 is a key Rho kinase target necessary for the local concentration of E-cadherin at cell-cell contacts
- PMID: 16030252
- PMCID: PMC1237062
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0330
Myosin 2 is a key Rho kinase target necessary for the local concentration of E-cadherin at cell-cell contacts
Abstract
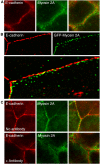
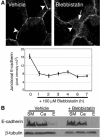
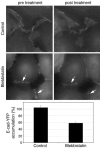
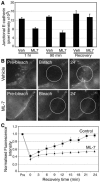
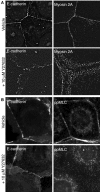
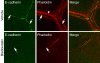
Classical cadherins accumulate at cell-cell contacts as a characteristic response to productive adhesive ligation. Such local accumulation of cadherins is a developmentally regulated process that supports cell adhesiveness and cell-cell cohesion. Yet the molecular effectors responsible for cadherin accumulation remain incompletely understood. We now report that Myosin 2 is critical for cells to concentrate E-cadherin at cell-cell contacts. Myosin 2 is found at cadherin-based cell-cell contacts and its recruitment requires E-cadherin activity. Indeed, both Myosin 2 recruitment and its activation were stimulated by E-cadherin homophilic ligation alone. Inhibition of Myosin 2 activity by blebbistatin or ML-7 rapidly impaired the ability of cells to concentrate E-cadherin at adhesive contacts, accompanied by decreased cadherin-based cell adhesiveness. The total surface expression of cadherins was unaffected, suggesting that Myosin 2 principally regulates the regional distribution of cadherins at the cell surface. The recruitment of Myosin 2 to cadherin contacts, and its activation, required Rho kinase; furthermore, inhibition of Rho kinase signaling effectively phenocopied the effects of Myosin 2 inhibition. We propose that Myosin 2 is a key effector of Rho-Rho kinase signaling that regulates cell-cell adhesion by determining the ability of cells to concentrate cadherins at contacts in response to homophilic ligation.
Figures




References
-
- Amano, M., Ito, M., Kimura, K., Fukata, Y., Chihara, K., Nakano, T., Matsuura, Y., and Kaibuchi, K. (1996). Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Bertet, C., Sulak, L., and Lecuit, T. (2004). Myosin-dependent junction remodelling controls planar cell intercalation and axis elongation. Nature 429, 667–671. - PubMed
-
- Boggon, T. J., Murray, J., Chappuis-Flament, S., Wong, E., Gumbiner, B. M., and Shapiro, L. (2002). C-cadherin ectodomain structure and implications for cell adhesion mechanisms. Science 296, 1308–1313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

