Evaluation of pharmacological treatment of impulsivity in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- PMID: 16033162
- PMCID: PMC1226151
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2005.116-02
Evaluation of pharmacological treatment of impulsivity in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Abstract
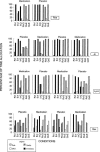
We used an assessment that involved competing reinforcer dimensions in a concurrent-schedules arrangement to examine the effects of stimulant medication on impulsivity (i.e., sensitivity of choices to reinforcer immediacy relative to rate, quality, and effort) with 4 students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The assessments were administered in the context of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, counterbalanced reversal design. Reinforcer immediacy was the most influential dimension for 3 of the students and the second most influential dimension for 1 of the students across placebo and medication conditions; medication did not affect these sensitivities.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington DC: Author; 2000. (4th ed.)
-
- Angello L.M, Volpe R.J, DiPerna J.C, Gureasko-Moore S.P, Gureasko-Moore D.P, Nebrig M.R, et al. Assessment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: An evaluation of six published rating scales. School Psychology Review. 2003;32:241–262.
-
- Atkins M.S, Pelham W.E. School-based assessment of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Learning Disabilities. 1991;24:197–225. - PubMed
-
- Barkley R.A. ADHD and the nature of self-control. New York: Guilford; 1997.
-
- Barkley R.A. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. New York: Guilford; 1998. (2nd ed.)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

