Interaction of reinforcement schedules, a behavioral prosthesis, and work-related behavior in adults with mental retardation
- PMID: 16033164
- PMCID: PMC1226153
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2005.9-04
Interaction of reinforcement schedules, a behavioral prosthesis, and work-related behavior in adults with mental retardation
Abstract
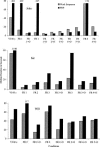
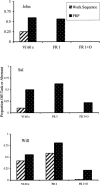
The effects of variable-interval (VI) and fixed-ratio (FR) schedules of reinforcement for work-related behavior and an organizer for the work materials (behavioral prosthesis) were evaluated with 3 adults with severe or profound mental retardation. The participants had been recommended for study because of high rates of off-task and aberrant behavior in their daily vocational training programs. For 2 participants, VI and FR schedules resulted in the same outcome: more aberrant behavior than on-task and off-task behavior combined. The FR schedule nearly eliminated emission of aberrant and off-task behavior by the 3rd participant. Combining the behavioral prosthesis with FR reinforcement (FR+O) increased the proportion of time spent in on-task behavior by all participants under certain FR schedule parameters. Second-by-second analyses of the observation records revealed that FR schedules reduced off-task and aberrant behavior during work sequences (i.e., ratio runs), and FR+O led to a further reduction of these behaviors during postreinforcement pauses. Overall, the results show how organizer and schedule parameters can be adjusted to produce an optimized balance between productivity and reinforcement while undesirable behavior is minimized.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparison of dense-to-lean and fixed lean schedules of alternative reinforcement and extinction.J Appl Behav Anal. 2004 Fall;37(3):323-38. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2004.37-323. J Appl Behav Anal. 2004. PMID: 15529889 Free PMC article.
-
Reinforcement schedule thinning following treatment with functional communication training.J Appl Behav Anal. 2001 Spring;34(1):17-38. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2001.34-17. J Appl Behav Anal. 2001. PMID: 11317985 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-time schedules attenuate extinction-induced phenomena in the treatment of severe aberrant behavior.J Appl Behav Anal. 1998 Winter;31(4):529-42. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1998.31-529. J Appl Behav Anal. 1998. PMID: 9891392 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of reinforcement schedules in the reduction of stereotypy with supported routines.Res Dev Disabil. 1998 Mar-Apr;19(2):99-122. doi: 10.1016/s0891-4222(97)00045-0. Res Dev Disabil. 1998. PMID: 9547523
-
Supporting individuals with intellectual disability and challenging behaviour in integrated work settings: an overview and a model for service provision.J Intellect Disabil Res. 1999 Feb;43 ( Pt 1):19-29. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2788.1999.43120169.x. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1999. PMID: 10088965 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of absolute and relative reinforcer value using progressive-ratio schedules.J Appl Behav Anal. 2008 Summer;41(2):189-202. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2008.41-189. J Appl Behav Anal. 2008. PMID: 18595283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Association on Mental Retardation. Mental retardation: Definition, classification, and systems of support. Washington, DC: Author; 1992.
-
- Azrin N.H, Kaplin S.J, Foxx R.M. Autism reversal: Eliminating stereotypic self-stimulation of retarded individuals. American Journal of Mental Deficiency. 1973;78:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Barmann B.C. Use of contingent vibration in the treatment of self-stimulatory hand-mouthing and ruminative vomiting behavior. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry. 1980;11:307–311.
-
- Barrett B.H. Behavior analysis. In: Wortis J, editor. Mental retardation and developmental disabilities. Oxford, England: Brunner Mazel; 1977. pp. 141–202. Vol. 9.
-
- Cataldo M.F, Ward E.M, Russo D.C, Riordan M, Bennett D. Compliance and correlated problem behavior in children: Effects of contingent and noncontingent reinforcement. Analysis and Intervention in Developmental Disabilities. 1986;6:265–282.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

