A genome-wide in situ hybridization map of RNA-binding proteins reveals anatomically restricted expression in the developing mouse brain
- PMID: 16033648
- PMCID: PMC1199591
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-5-14
A genome-wide in situ hybridization map of RNA-binding proteins reveals anatomically restricted expression in the developing mouse brain
Abstract
Background: In eukaryotic cells, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) contribute to gene expression by regulating the form, abundance, and stability of both coding and non-coding RNA. In the vertebrate brain, RBPs account for many distinctive features of RNA processing such as activity-dependent transcript localization and localized protein synthesis. Several RBPs with activities that are important for the proper function of adult brain have been identified, but how many RBPs exist and where these genes are expressed in the developing brain is uncharacterized.
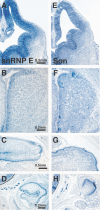
Results: Here we describe a comprehensive catalogue of the unique RBPs encoded in the mouse genome and provide an online database of RBP expression in developing brain. We identified 380 putative RBPs in the mouse genome. Using in situ hybridization, we visualized the expression of 323 of these RBP genes in the brains of developing mice at embryonic day 13.5, when critical fate choice decisions are made and at P0, when major structural components of the adult brain are apparent. We demonstrate i) that 16 of the 323 RBPs examined show neural-specific expression at the stages we examined, and ii) that a far larger subset (221) shows regionally restricted expression in the brain. Of the regionally restricted RBPs, we describe one group that is preferentially expressed in the E13.5 ventricular areas and a second group that shows spatially restricted expression in post-mitotic regions of the embryonic brain. Additionally, we find a subset of RBPs that share the same complex pattern of expression, in proliferating regions of the embryonic and postnatal NS and peripheral tissues.
Conclusion: Our data show that, in contrast to their proposed ubiquitous involvement in gene regulation, most RBPs are not uniformly expressed. Here we demonstrate the region-specific expression of RBPs in proliferating vs. post-mitotic brain regions as well as cell-type-specific RBP expression. We identify uncharacterized RBPs that exhibit neural-specific expression as well as novel RBPs that show expression in non-neural tissues. The data presented here and in an online database provide a visual filter for the functional analysis of individual RBPs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The mRNA-bound proteome of the early fly embryo.Genome Res. 2016 Jul;26(7):1000-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.200386.115. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 27197210 Free PMC article.
-
Human protein-RNA interaction network is highly stable across mammals.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 30;20(Suppl 12):1004. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6330-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31888461 Free PMC article.
-
Novel retinal genes discovered by mining the mouse embryonic RetinalExpress database.Mol Vis. 2004 Oct 8;10:773-86. Mol Vis. 2004. PMID: 15496829
-
RNA-binding proteins, neural development and the addictions.Genes Brain Behav. 2016 Jan;15(1):169-86. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12273. Genes Brain Behav. 2016. PMID: 26643147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
General RBP expression in human tissues as a function of age.Ageing Res Rev. 2012 Sep;11(4):423-31. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Feb 4. Ageing Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 22326651 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical cadherin, Fat2, regulates axon terminal organization in the developing Drosophila olfactory receptor neurons.iScience. 2024 Jun 21;27(7):110340. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110340. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39055932 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA nuclear export and human disease.Dis Model Mech. 2008 Sep-Oct;1(2-3):103-8. doi: 10.1242/dmm.000745. Dis Model Mech. 2008. PMID: 19048072 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation and cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-dependent mRNA regulation are involved in Xenopus retinal axon development.Neural Dev. 2009 Mar 2;4:8. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-4-8. Neural Dev. 2009. PMID: 19254368 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence search and analysis of gene products containing RNA recognition motifs in the human genome.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 22;15(1):1159. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1159. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25534245 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation of glutathione peroxidase 4 expression through guanine-rich sequence-binding factor 1 is essential for embryonic brain development.Genes Dev. 2008 Jul 1;22(13):1838-50. doi: 10.1101/gad.466308. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18593884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lasko P. Gene regulation at the RNA layer: RNA binding proteins in intercellular signaling networks. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:RE6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

