Lectin binding profiles of SSEA-4 enriched, pluripotent human embryonic stem cell surfaces
- PMID: 16033656
- PMCID: PMC1182361
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-5-15
Lectin binding profiles of SSEA-4 enriched, pluripotent human embryonic stem cell surfaces
Abstract
Background: Pluripotent human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) have the potential to form every cell type in the body. These cells must be appropriately characterized prior to differentiation studies or when defining characteristics of the pluripotent state. Some developmentally regulated cell surface antigens identified by monoclonal antibodies in a variety of species and stem cell types have proven to be side chains of membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins. Therefore, to examine hESC surfaces for other potential pluripotent markers, we used a panel of 14 lectins, which were chosen based on their specificity for a variety of carbohydrates and carbohydrate linkages, along with stage specific embryonic antigen-4 (SSEA-4), to determine binding quantitation by flow cytometry and binding localization in adherent colonies by immunocytochemistry.
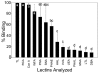
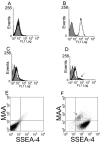
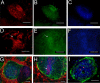
Results: Enriching cells for SSEA-4 expression increased the percentage of SSEA-4 positive cells to 98-99%. Using enriched high SSEA-4-expressing hESCs, we then analyzed the binding percentages of selected lectins and found a large variation in binding percentages ranging from 4% to 99% binding. Lycopersicon (tomato)esculetum lectin (TL), Ricinus communis agglutinin (RCA), and Concanavalin A (Con A) bound to SSEA-4 positive regions of hESCs and with similar binding percentages as SSEA-4. In contrast, we found Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA) and Lotus tetragonolobus lectin (LTL) did not bind to hESCs while Phaseolus vulgaris leuco-agglutinin (PHA-L), Vicia villosa agglutinin (VVA), Ulex europaeus agglutinin (UEA), Phaseolus vulgaris erythro-agglutinin (PHA-E), and Maackia amurensis agglutinin (MAA) bound partially to hESCs. These binding percentages correlated well with immunocytochemistry results.
Conclusion: Our results provide information about types of carbohydrates and carbohydrate linkages found on pluripotent hESC surfaces. We propose that TL, RCA and Con A may be used as markers that are associated with the pluripotent state of hESCs because binding percentages and binding localization of these lectins are similar to those of SSEA-4. Non-binding lectins, DBA and LTL, may identify differentiated cell types; however, we did not find these lectins to bind to pluripotent SSEA-4 positive hESCs. This work represents a fundamental base to systematically classify pluripotent hESCs, and in future studies these lectins may be used to distinguish differentiated hESC types based on glycan presentation that accompanies differentiation.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

